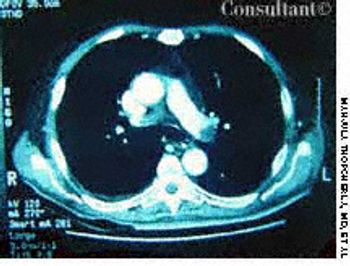
A 52-year-old woman who was undergoing chemotherapy for lymphoma was admitted to the hospital with fever of a few days' duration. The patient had smoked cigarettes for many years; she had no history of deep venous thrombosis.
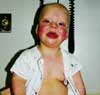

A 52-year-old woman who was undergoing chemotherapy for lymphoma was admitted to the hospital with fever of a few days' duration. The patient had smoked cigarettes for many years; she had no history of deep venous thrombosis.
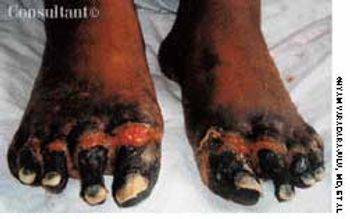
A 21-year-old man slept in a car in upstate New York for three winter nights. Discomfort and swelling of his toes developed, which progressed to marked discoloration of the digits.
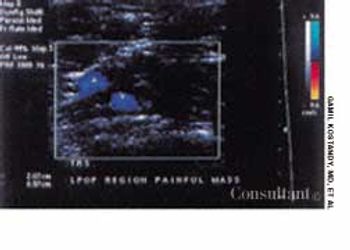
A 47-year-old woman complained of pain and swelling of the right knee of 3 days' duration. Positive fullness of the popliteal area with no pulsations was discerned. Doppler ultrasound showed a 2.5 cm × 1.5 cm cystic structure in the right popliteal region; this confirmed the diagnosis of a Baker's cyst.
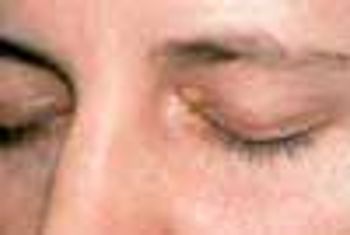
A 49-year-old woman noticed a growing lesion near the inner corner of her left upper eyelid. The lesion had become conspicuous because of its size and color; the patient wanted it removed.
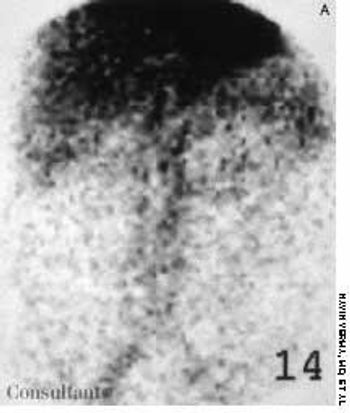
A 56-year-old man who had hematuria for 2 weeks underwent ultrasonography. This disclosed a well-circumscribed cyst in the lower pole of the left kidney and echogenic foci in the upper pole of the right kidney, without any evidence of posterior shadowing. A hyperechoic, well-circumscribed, circular focus was also seen in the right lobe of the liver. Abdominal CT confirmed the presence of a left renal cyst and revealed a 4.7-cm hypodense lesion in the right lobe of the liver, which suggested hemangioma.
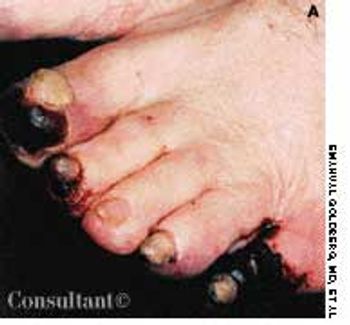
Four months after coronary artery bypass surgery, a 77-year-old man began to suffer severe pain in his feet. Multiple necrotic areas developed on the toes.
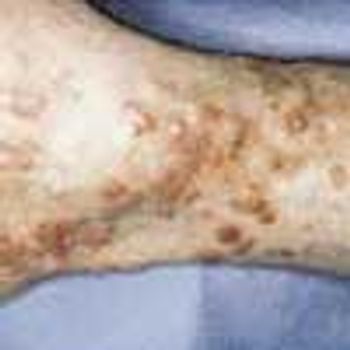
Erythema elevatum diutinum (EED) is a rare and usually chronic form of vasculitis. It has been postulated that EED is the result of immune complex formation in small vessels secondary to some antigenic stimulation.
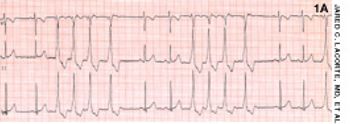
An 8-year-old boy was brought to his pediatrician for well-child care. On physical examination, an irregularly irregular heart rate was detected.
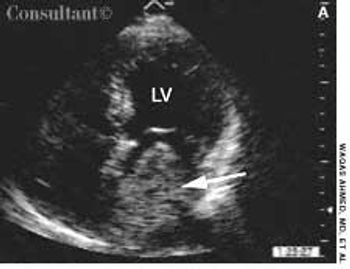
For 2 years, a 60-year-old woman with long-standing hypertension had experienced worsening dizzy spells, fatigue, and chest discomfort. She also had cold extremities, significant dyspnea on exertion, and orthopnea. The patient was taking amlodipine and furosemide.
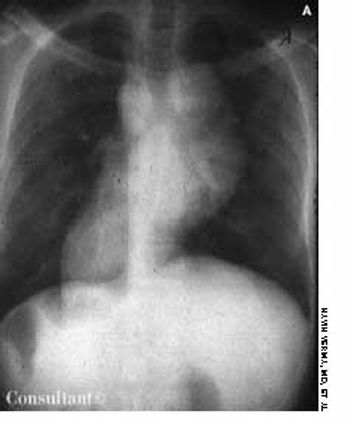
For the past year, a 45-year-old man experienced dull, aching chest pain and breathlessness following routine work. He had no history of fever, cough, dysphagia, or change in voice.
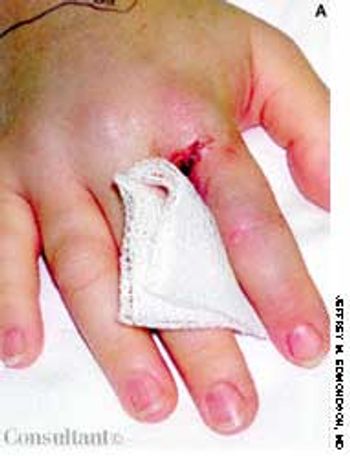
While working in her garden in Virginia, a 40-year-old woman felt a sudden, sharp pain between the fingers of her right h and saw blood coming from an open wound. Immediately, she experienced a burning sensation at the site and noticed numbness and swelling in the hand. The patient was rushed to the emergency department.
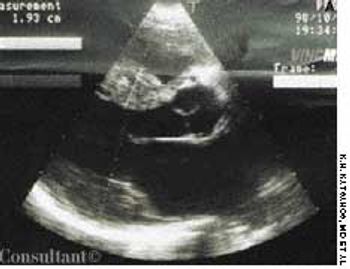
Dyspnea, orthopnea, and weight loss sent a 40-year-old woman for medical consultation. Fifteen years earlier, the patient had been nephrectomized because of left kidney lithiasis. There was no history of other symptoms or diseases.
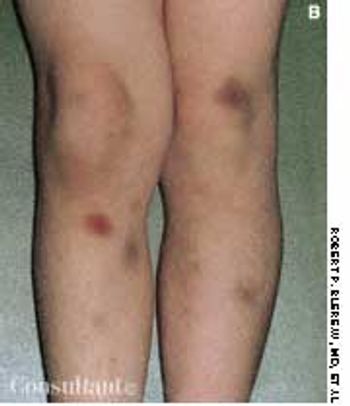
A mother, fearing that her 4-year-old son had been abused at his day-care center, rushed him to the emergency department, where an evaluation revealed a platelet count of 1,000/µL. Except for bruises on the boy's face and legs, the physical findings were normal. Bone marrow aspiration showed numerous megakaryocytes and was otherwise normal. The youngster's history included treatment for bronchitis, sinusitis, and conjunctivitis 2 weeks earlier.
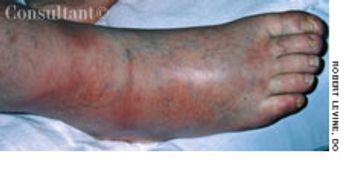
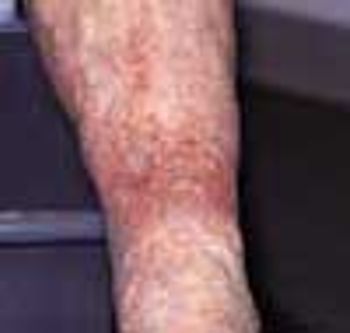
A mildly painful, nonpruritic rash on the forearms and legs prompted a 42-year-old man to go to the emergency department (ED). The patient noted the rash when he awoke that morning. He had had joint pain and fever for the past 7 days and generalized malaise with chills that began about 3 days earlier. He had no significant medical history.
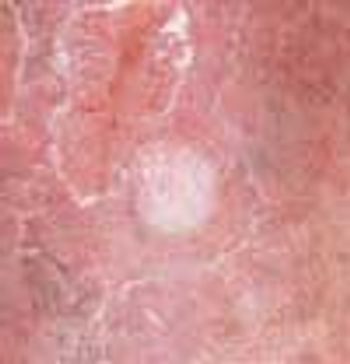
A 57-year-old man with a history of venous stasis leg ulceration wondered about the “white spots” on his leg.
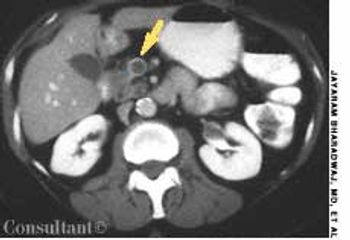
A 65-year-old woman with metastatic adenocarcinoma of the colon was undergoing chemotherapy following a colectomy and a hepatic wedge resection. The physical examination and laboratory data were unremarkable.
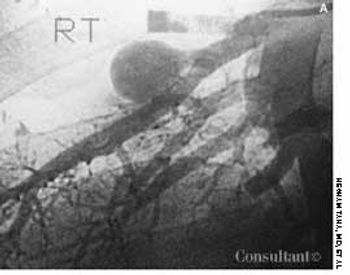
Tortuous, dilated varicosities; multiple smaller caliber abnormal perforating vessels; and chronic brawny edema of chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) were seen on a 70-year-old man's left leg. He reported that the edema and discoloration had worsened over the last 15 years. The brawny edema stopped just above the ankle, indicating that compression by the patient's sock controlled the signs and symptoms of CVI.
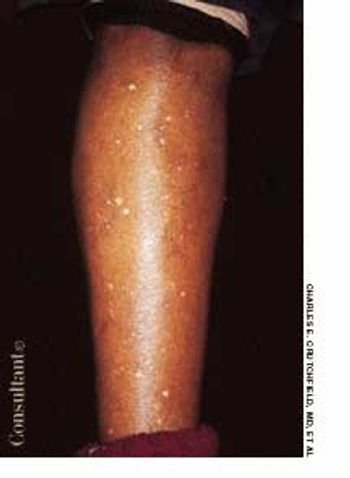
After more than 15 years of wondering what the “white specks” on his legs were, a 64-year-old man consulted his physician. The patient was taking medication to control hypertension; he was otherwise healthy.
A 22-year-old man complained of progressive shortness of breath and abdominal distention. Three years before, he had completed chemotherapy for Hodgkin's disease and had since been in remission. Recently, he had been treated for tonsillitis with oral antibiotics.
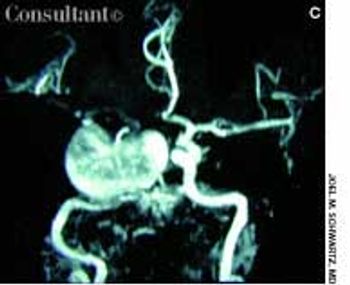
Increasingly frequent headaches and blurred vision had affected a 74-year-old woman for several months. Double vision, which initially occurred only when the patient looked to the right, had started to affect vision when she looked straight ahead. Her eye movements when looking to the left were normal; the right eye, however, did not go beyond midline when looking to the right. Upward and downward gaze were not affected.
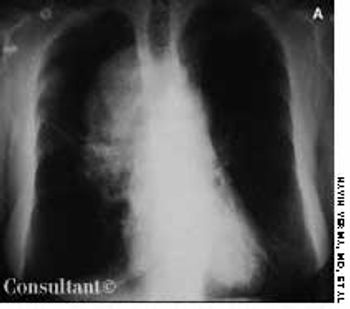
A 42-year-old woman complained of facial puffiness, fullness, and redness for 2 weeks, which were gradually becoming more severe. She also noticed a sensation of “heaviness” in her head. The patient had no significant past medical history. She denied having a cough, shortness of breath, hoarseness, allergies of any kind, and neurologic deficits. Her weight and appetite were unchanged. She had smoked a pack of cigarettes every day for the past 20 years.
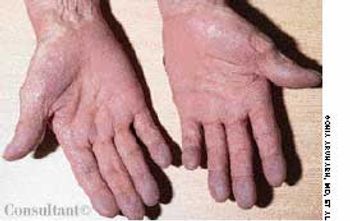
The significant palmar erythema seen on the hands of a 60-year-old man with alcoholic cirrhosis is a sign of underlying chronic liver failure.
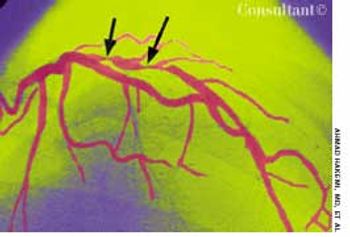
Coronary angiography was performed in a 54-year-old man with low-level stable angina. He had undergone percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) 3 months earlier. The angiogram showed tight stenosis of the proximal left anterior descending artery. The lesion was successfully dilated during a second PTCA, and a stent was placed using a flexible catheter.
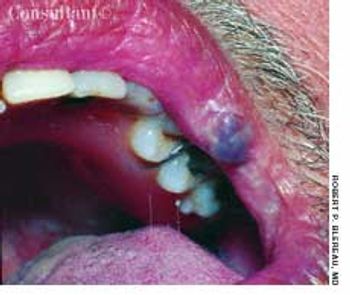
For 3 years, a gradually enlarging, raised, purple, cystic lesion had been present on the left upper lip vermilion of a 51-year-old man. The asymptomatic lesion measured 0.5 cm in diameter. The patient was given a local anesthetic, and the lesion was excised by wedge resection in the office; pathologic examination confirmed the diagnosis of benign cavernous hemangioma.
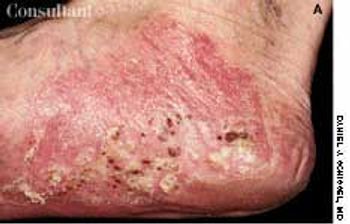
A 68-year-old woman was referred from an acute care clinic for evaluation of a persistent cellulitis. Ten days before, erythematous, pruritic plaques developed on her ankles; these slowly enlarged, and pustules formed. The patient denied fever or chills. Her past medical history was unremarkable, and conjugated estrogen, medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets, and multivitamins were the only medications and nutritional supplements she was taking.