
Researchers developed polygenic risk scores for 6 common diseases and informational resources to help primary care physicians incorporate them into clinical practice.

Researchers developed polygenic risk scores for 6 common diseases and informational resources to help primary care physicians incorporate them into clinical practice.
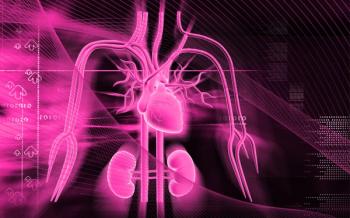
In patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease with and without history of CVD, finerenone was associated with improved CV and kidney outcomes.
DiabetesWise Pro, created at Stanford University, provides an unbranded, unbiased guide to matching diabetes technology to patient needs, access, and lifestyle.

Initiating diabetes technology of any kind is a big step for patients, but also for a lot of primary care clinicians. If you have concerns, these myths and facts are for you.

Moderate consumption of alcohol with food was significantly associated with a 14% lower risk of type 2 diabetes in a preliminary analysis.

t:slim X2 insulin pump users can now program or cancel bolus dosing with the secure t:connect mobile app already on their phones, says Tandem Diabetes Care.
Researchers in Taiwan found NOACs were associated with lower hazards of diabetes complications. and death than warfarin in persons with AF and DM.

The 180-day sensor life doubles the period of continuous use and cuts in half the number of CGM removals and reinsertions, without loss of accuracy.
Tirzepatide at 3 different doses significantly improved glycemic control and promoted weight loss when added to titrated insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes.

NYU endocrinologist Brian Levy, MD, offers perspective on keeping the transition from basal insulin to multiple daily injections as simple as possible for patient and provider.

Type 2 diabetes patients-and their PCPs-may have trouble moving to basal + mealtime insulin from basal insulin alone. Endocrinologist Brian Levy, MD, offers insights.

The American Academy of Neurology recently issued a guideline on oral and topical treatments for painful diabetic neuropathy. Here, a concise summary for clinicians.

Glucose and insulin levels decreased after just 3 minutes of the moderate-intensity exercise, a promising finding for those with type 2 diabetes, say authors of a new study.

Available therapies combined with new approaches that address social determinants of health and other barriers to care can help, suggests new statement.

WATCH: The FDA approval of semaglutide 2.4 mg for adults with obesity was "by far the big event in 2021," said Donna Ryan, MD. More from our look back/look ahead interview, here.
The ADA's annual update to its comprehensive evidence-based standards includes new guidance on diabetes screening, first-line therapies, and comorbid NAFLD/NASH.

CGMs have revolutionized diabetes management for patients and healthcare providers alike. This slide show summarizes the most recent enhancements.

Get a quick look at 12 of the many FDA-approved drugs in 2021 for conditions commonly seen in primary care.

ADA 2021 Scientific Sessions recap, tests of clinical knowledge, expert interviews, and more in this roundup from Patient Care Online.

Weight loss and disease remission in T2D may differ between patients regardless of type of diet regimen chosen, say authors of a new analysis.

Among patients with diabetes, over 50% of statin users experienced diabetes progression vs 48% of non-statin users, according to a retrospective matched-cohort study.

EASD 2021: First analysis of its kind found COVID-19-induced lockdown was associated with improved glycemic control among patients with T1D, but not T2D.

From 2001 to 2017, the estimated prevalence of youth-onset T1D and T2D increased approximately 45% and 95%, respectively, according to a new study.
Low-income patients with diabetes enrolled in high-deductible health plans used less preventive and primary care services and more emergency visits, suggests new review.

Take this quick quiz to test your knowledge of key findings in landmark studies on the cardioprotective effects of SGLT2i and GLP-1 RAs.