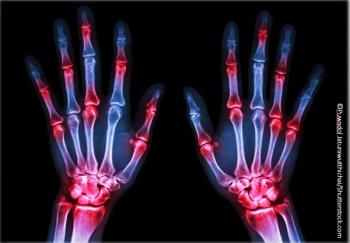
RA can be managed in primary care but comes with unique challenges. Here, strategies outlined at the ACP Internal Medicine Meeting 2018.

RA can be managed in primary care but comes with unique challenges. Here, strategies outlined at the ACP Internal Medicine Meeting 2018.

Are dairy products really all that bad for cardiovascular health? One new study suggests otherwise. Scroll through our slideshow to find out more.
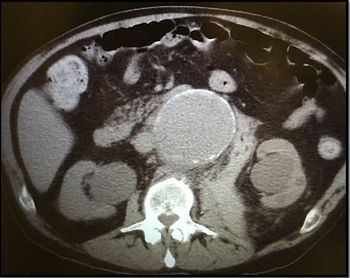
In the ED the patient says the shortness of breath began the night before after he took ibuprofen for a flare of back pain. Is there a connection?

What does the latest research show on obesity? Scroll through our slideshow to see what three recent studies found on obesity.

Do you know what percentage of US adults report binge drinking? Or how much alcohol sold is consumed while binge drinking? Take our 12-question quiz to find out.
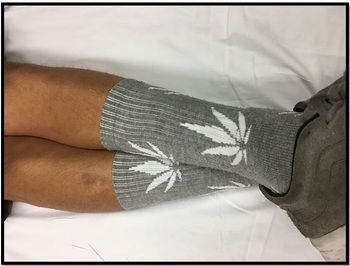
Sudden onset of difficulty breathing, dry mouth, and stiff, swollen neck and throat. . . what diagnostic clue do the patient's socks offer, and what action should follow?

How much do you know about e-cigarettes? Take our 10-question quiz to put your knowledge to the test.

The role of benziodiazepines in the opioid epidemic is largely overlooked. What do you know about the role of these agents in the mounting number of overdoses and deaths?

We top-line 5 migraine tracking & management apps that stand out from the many available and our app reviewer points out defining features.

Are you up-to-date on the wide variety and variable potency of cannabis products your patients may use? Test yourself and find out.

What does primary care compensation look like these days? Would you choose primary care all over again? Here: key highlights that shed light from a Medscape Physician Compensation Report.
Here: a quick overview of updates to the diagnosis and treatment of osteoporosis.

January 12, 2018 was a busy day for health care headlines. See what you recall from 3 news stories on 1/12/18 (and a bonus story from 1/10/18).

Can a physician's age affect treatment outcome? It did in this study of hospitalized elderly patients.
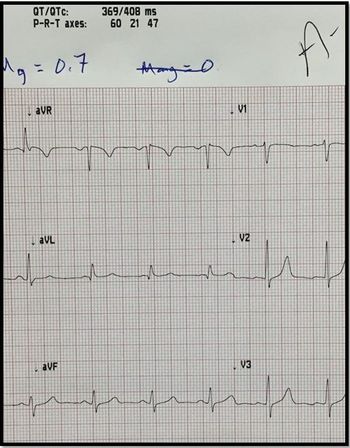
This 43-year-old man has known alcohol addiction but has never had post-withdrawal leg weakness. What tests would you order to Dx cause?
For PCPs, now poised to play a bigger role in screening and care for patients with HCV, we highlight 10 forces reshaping the HCV landscape.

Methadone and buprenorphine are underutilized as treatment for opioid addiction. Is one safer? More effective? More convenient? Take the quiz.
Our app reviewer toplines the Pixel 2 features that busy PCPs need most. Brand allegiance aside, aren't new smartphone features always worth a look?

Newest news on coffee, from BMJ: "...more likely to benefit health than to harm it..." High vs low intake reduces risk of diabetes and Alzheimer disease. Plus, more.
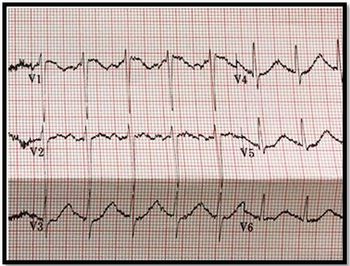
Physical exam, including vitals, is normal although patient is tremulous. Blood sent for labs, so look for clues in the ECG.