Diabetes, obesity, hyperlipidemia, hypothyroidism-these endocrine disorders and others are major reasons why patients come to you. Find out what you know, and don’t know, here.

Diabetes, obesity, hyperlipidemia, hypothyroidism-these endocrine disorders and others are major reasons why patients come to you. Find out what you know, and don’t know, here.

The ADA recommends GLP-1 agonists as second-line therapy against type 2 diabetes. What makes this class unique in its impact on hyperglycemia?

Metabolic disorders in patients with diabetes place them at particularly high risk for CV morbidity. Find insights on Dx and Tx in these slides.
What brings patients to your office-and not the specialty office down the street? Insights in this slideshow.

The ADA provides an abridged version for PCPs of its annual Standards of Medical Care. Our slides summarize 6 updates important to primary care.

The drug appeared to reduce the risk in the first study to assess its effects on younger patients with diabetes in the United States.



Take this 3-question mini-quiz to see if you’re up-to-date on diabetes and breast cancer risk, gestational diabetes and depression, and sedentary time and diabetes development.



Three questions for you about this week's breaking medical news on the risks of sitting still, diabetic eye disease, and antibiotics and insulin resistance.

Here’s a look at what’s new and interesting on the Web for health care professionals.

Evidence-based recommendations on the intake of free sugars to reduce the risk of noncommunicable diseases are the ingredients of a new WHO guideline. Find the recipe in these slides.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists represent a novel class of antihyperglycemic agents that have a cardiac-friendly profile.

Examining ethnic patterns of prevalent geriatric conditions in diabetes may help ensure culturally competent, patient-centered care in an increasingly diverse population.
At least some of the genes regulate insulin action on sugar uptake. The take-aways: insights into potential targets for diabetes treatment and more hope for prevention.

The risk may be greater in patients who are younger, new to the disease, and receiving few other medications-good information for targeting interventions.

The reasons reflect the silence that surrounds depression, its basic invisibility, and the mistaken notion that it can't be dealt with in primary care.

The risk is lowered more in minority women than in white women with a healthy diet, which can play a vital role in prevention.

Maintaining tight glycemic control in older diabetic adults who are in poor health can do far more harm than good, according to results of a new study.

Recommendations from the American Diabetes Association also suggest a less stringent diastolic blood pressure target, all in keeping with recent changes in cardiovascular risk management guidelines.
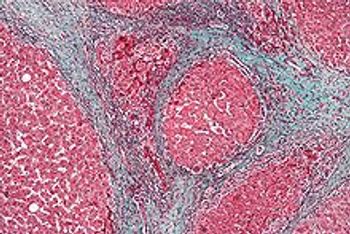
Continuing metformin after a diagnosis of cirrhosis can significantly decrease the risk of death in patients with diabetes, a new study suggests.

Drugs, diseases, guidelines, databases-all at the touch of an app. Here: a selection of smartphone/tablet applications that may make your clinical practice a little easier this coming year.

New drugs that treat stubborn illness seen often in primary care lead this group of Top 5 Papers for 2014. Type 2 diabetes, cryptogenic stroke, and hep-C are key targets.