Diabetes is a progressive disease and takes advantage of inaction. How would you manage our patient Mrs Davis?

Diabetes is a progressive disease and takes advantage of inaction. How would you manage our patient Mrs Davis?
Who is at risk for T2DM? How often should you screen? What are the cut offs for Dx? Revisit the basics in 5 minutes or less.

The Numbers: >90% of US adults aged ≥65 yrs have diabetes; 33% of those have T2DM; ~50% of older adults have prediabetes. We highlight new Endocrine Society treatment guidance.

More than one-third of those in recovery from drug/alcohol use have chronic physical disease. A novel study looks at prevalence of health issues by type of substance used.

From a mobile EKG monitor to a digital urinalysis app, these medical "devices" are changing the way healthcare is delivered.

Find out what you know about which diabetes drugs in which classes show CV protective properties and results of the trials that support their use.

Findings: a heart-healthy lifestyle reduces DM risk; 1 egg a day may protect against T2DM; and a new genetic risk score may improve DM diagnosis.

True or false? The rates of T2DM in people with SMI are up to 5 times higher vs the general population.
Help your patients with diabetes help themselves. See 5 apps at-a-glance you can discuss at the next visit.
Sample: True or false? The prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes is higher among obese adults vs overweight adults.
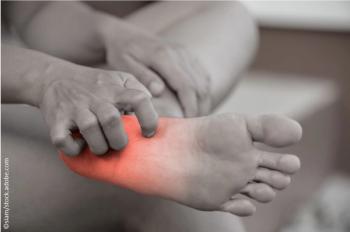
Up to 50% of patients with diabetes may have signficant neuropathy, yet be asymptomatic. Here's how to avoid or attenuate the condition.
Severe hypoglycemia was associated with death within ~1 week among patients with T2DM, according to a subanalysis of the LEADER trial.

True or False: In 2015, Americans spent more on insulin glargine than any other drug. The answer and 9 more questions in our quiz.

Results include: The metabolic dangers of neuroleptic Rx in youth; prevalence of T2DM in minorities with severe mental illness; and gaps in care for mentally ill with T2DM.

Anything less than comprehensive care for type 2 diabetes is quickly becoming old school.

What to do when patients face their own "clinical inertia"? Here, 3 simple ways to help them push through.

Severe hypoglycemia is more prevalent than previously believed and also significantly underreported. Details from 3 studies at ADA 2018.

From ADA 2018: Two new biomarkers predict CV events independently of conventional risk factors, plus post-hoc analysis of VADT.

What is the impact on insulin dose, A1c, body weight of adding GLP-1 RA to a MDI insulin regimen? Three studies from ADA 2018 illuminate.

Three studies at ADA 2018 highlight the current track record of SGLT-2is in reducing CV-related morbidity and mortality.

Should you: Stop a DPP-4i when you start insulin? Prescribe initial triple combination Rx? What about SGLT2i + DPP-4i + MET vs insulin + MET? Find out.

How do 2nd generation basal insulin formulations perform vs their predecessors? We report highlights of 3 important studies from the ADA 78th Scientific Sessions.

Highlights include: POC A1c testing in prediabetes screening, first-year weight loss after bariatric surgery, and predicting fracture risk in obese patients.

A tooth-mounted sensor, a glucose monitor built into a smartphone case, plus 3 more new “gee whiz” devices that could transform diabetes care.

Hypoglycemic episodes are uncomfortable, disruptive, and dangerous; 3 ways to help T2DM patients avoid and also correct them.