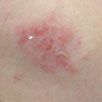
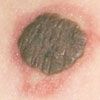
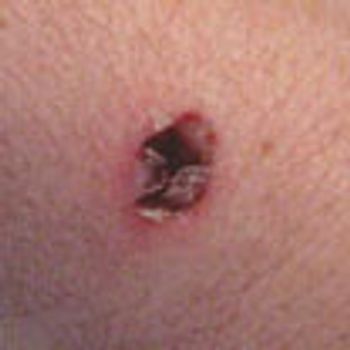
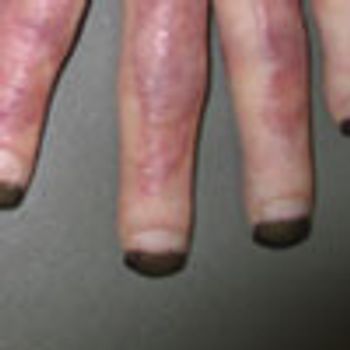
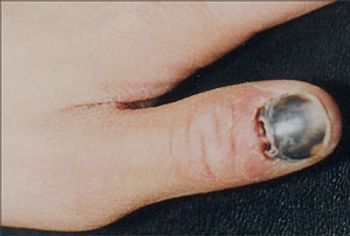
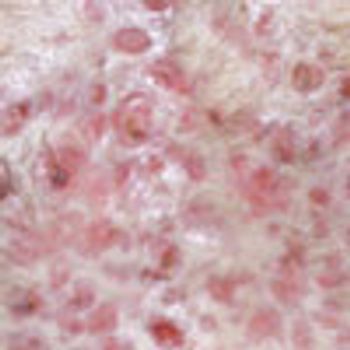
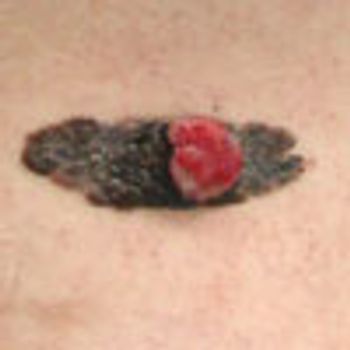
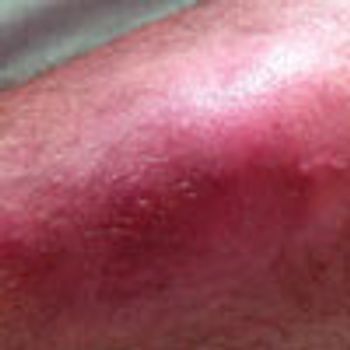
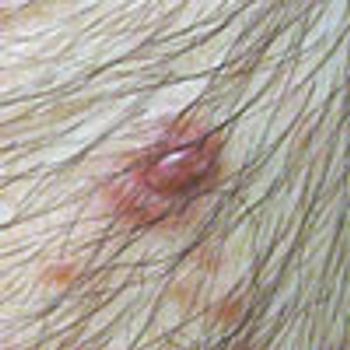
For several years, a 71-year-old man has had a mildly pruritic rash on his legs that develops every winter and resolves when the weather becomes warmer. He is scheduled to undergo knee surgery, but the surgeon refuses to perform the operation until the rash has cleared.