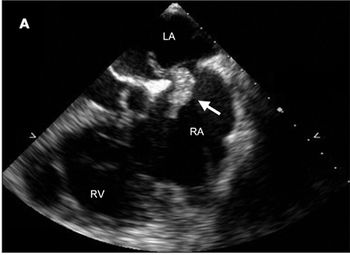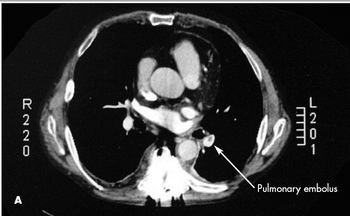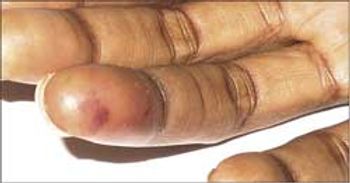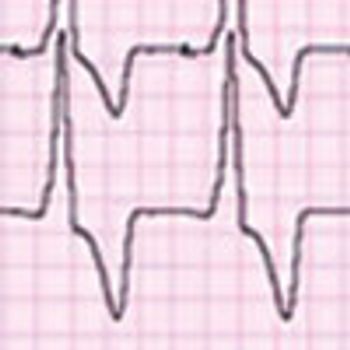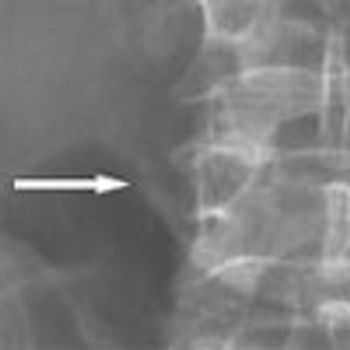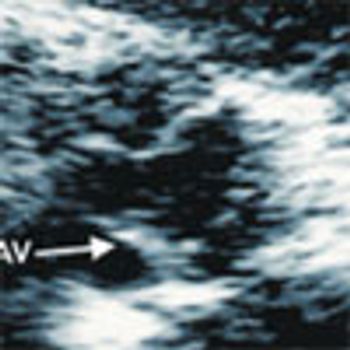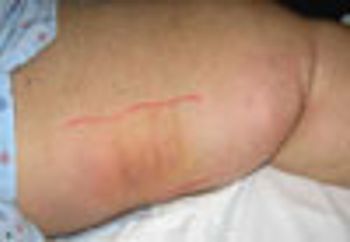
Up to 40% of patients who present with what may look like simple, isolated superficial venous thrombosis have concomitant deep venous thrombosis. This finding has led clinicians to first rule out DVT bilaterally via compression Doppler ultrasonography before treatment is considered.