
Dizzy patient? Their brain might not be getting enough blood, thanks to their antihypertensive dosage.

Dizzy patient? Their brain might not be getting enough blood, thanks to their antihypertensive dosage.
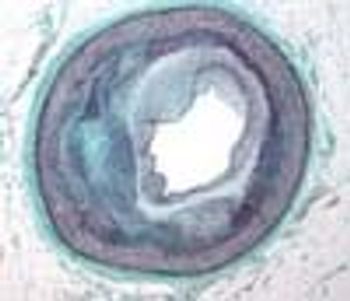
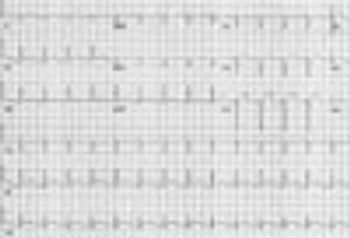
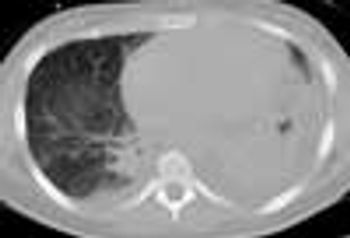

A recent commentary of mine regarding hypertension was entitled, “Are Prescribing Practices for Antihypertensives Primitive? The Truth Hurts."
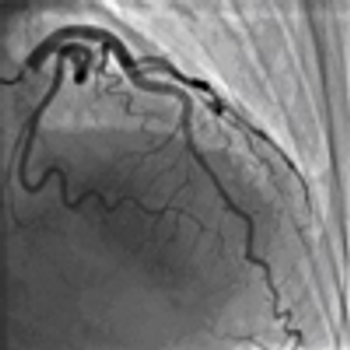
A 48-year-old African American man with no significant medical history sustained a gunshot wound to the face and shoulder.

Exercising at least 4 times a week can increase left ventricular mass and preserve elasticity, thereby reducing the risk of diastolic heart failure. Researchers from Texas presented their study results at the American College of Cardiology’s 60th Annual Scientific Session.

Measurement of pulse pressure may help identify patients with "white coat" hypertension, according to data presented by Korean researchers at the American College of Cardiology’s 60th Annual Scientific Session.

What is the optimal duration for antiplatelet therapy after placement of drug-eluting stents? Initial results of the EXCELLENT study show that 6 months of antiplatelet therapy is as effective as the 12-month regimen recommended by current guidelines.

A Danish study found no clinical benefit from using NT-proBNP (b-type natriuretic peptide) to identify and monitor high-risk patients with chronic heart failure, according to research from the NorthStar study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s 60th Annual Scientific Session in New Orleans.

Compared with medical therapy alone, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) significantly reduced cardiovascular deaths and the composite end point of all-cause deaths and cardiovascular-related hospitalizations, reported investigators from the Surgical Treatment of Ischemic Heart Failure (STICH) trial. However, the effect of the two management strategies on overall survival in patients with ischemic heart failure was similar.

Recently, the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA) released a focused update to the 2007 guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina (UA)/non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (non-STEMI).

A panel of experts presented a general strategy for evaluating patients with refractory hypertension, but ultimately cautioned the audience to assume non-compliance until proven otherwise.

The panel presented three challenging cases of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFPEF) (see Update on Diastolic Heart Failure). In an innovative twist, the panel solicited feedback from a standing-room-only audience through SmartPhone technology-attendees voted for their favored diagnostic approach, therapy, or final diagnosis, with voting results instantly integrated into the presenter’s Powerpoint display.

Diastolic heart failure (or HFPEF-heart failure with preserved ejection fraction) is characterized by inadequate myocardial relaxation and diastolic filling ("stiff ventricle"), with heart failure signs and symptoms despite normal ejection fraction. The most common cause is long-standing hypertension.

Systemic inflammation has been identified as a risk factor for the development of heart failure in population studies. In the 5-year prospective MESA study, researchers from Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore recorded a baseline nonspecific marker of systemic inflammation, C-reactive protein (CRP).

Researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston presented results from the PROTECT (ProBNP Outpatient Tailored Chronic Heart Failure) study. NT-proBNP (b-type natriuretic peptide) is a biomarker released from myocardial tissue in response to high levels of wall stretch and has been studied as a marker for decompensated systolic heart failure.

Global humanitarian James Orbinski, MD, will deliver the Franz M. Groedel Presidential Plenary Lecture at this year's Scientific Showcase Session on Sunday, April 3.

On December 18, 2005, Ariel Sharon, Prime Minister of Israel, experienced the sudden onset of aphasia. Despite being overweight, he had none of the traditional risk factors for cerebrovascular disease-hypertension, history of smoking, diabetes, or elevated cholesterol levels.

A 50-year-old man was brought to the emergency department (ED) after a witnessed syncopal event. He was awake but confused and unable to provide a history.
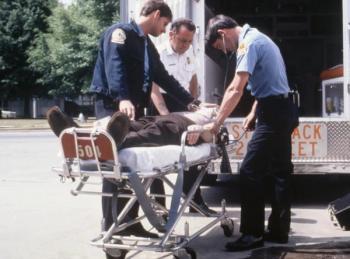
Recently, my wife and I received a gift certificate for one of our favorite restaurants, and we wasted no time in using it. The food and conversation were delightful, and the meal turned out to be exciting and enlightening on many levels. A patron of the restaurant, who was celebrating his 55th wedding anniversary, sustained a witnessed, public cardiac arrest. The experience led to an analysis of my involvement in the resuscitation.

Analysis of a number of studies led to a practical suggestion: persons at known risk for myocardial infarction (MI) as well as older adults should carry a few tablets of soluble aspirin with them at all times, and they should chew and swallow the tablets in the event of chest pain-the earlier the better.

Sitting in front of a TV or computer for long periods can raise the risk of cardiovascular disease and death, reported investigators recently in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. The risk does not appear to be offset by physical activity.

Yes, ACE inhibitors should be used with caution in patients with acute renal injury and high-grade renal vascular lesions, but these drugs are designed to help, not hurt kidneys. Now fast forward to another caveat: avoid or discontinue statins in patients who have elevated liver enzyme levels. Get ready for a therapeutic paradigm shift.
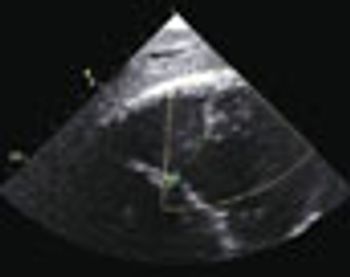
A previously healthy 55-year-old woman complained of fever, weakness, and generalized malaise for the past 3 to 4 weeks. She had been treated with ciprofloxacin, amoxicillin, and azithromycin for 21 days with no resolution of her symptoms. Five days before she was hospitalized, multiple nonspecific constitutional complaints developed.