
Identifying the cause of a persistent, asymptomatic aminotransferase elevation can be challenging. The possible diagnoses are many and varied. To narrow the differential, begin with a detailed history.

Identifying the cause of a persistent, asymptomatic aminotransferase elevation can be challenging. The possible diagnoses are many and varied. To narrow the differential, begin with a detailed history.

Treatment of hypertension can minimize both microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes and helps prevent nephropathy and cardiovascular events.

For 2 weeks, a 43-year-old white female had worsening nausea and multiple episodes of vomiting. Her symptoms began with increased malaise and decreased appetite. The emesis was unrelated to meals and was sometimes accompanied by mild abdominal distention. She had occasional fevers but denied any recent contact with ill persons. She also reported a 12-lb weight loss, decreased energy level, and an increased tan complexion over the past several months.

For 6 weeks, a 56-year-old man had worsening dyspnea on exertion and a cough productive of yellow sputum with scant hemoptysis. He reported subjective fever over the past month but no weight loss.

A 69-year-old woman with a protuberant abdomen presents with intermittent, painless vaginal bleeding of 2 weeks' duration. The patient has not seen a physician in years. Her abdominal girth began to increase 8 years ago.

A 74-year-old woman presented with a refractory pruritic eruption. Four months earlier, she had sought evaluation of a thickened, slightly crusted 6 3 8-cm patch on her right ankle of 2 months' duration. Contact dermatitis with secondary impetigo from scratching was suspected, and a topical corticosteroid and an oral antibiotic were prescribed.
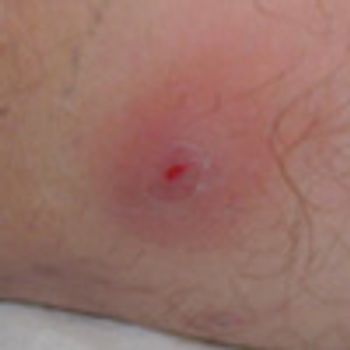
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic acneiform infection of the cutaneous apocrine glands.

Over the past 20 years, the treatment armamentarium for diabetes has greatly expanded: 8 different classes of non-insulin drugs and 8 different types of insulin are now available. The newer classes of agents include disaccharidase inhibitors, thiazolidinediones, meglitinides, glucagonlike peptide analogs, and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors.

PITTSBURGH, Oct. 15 -- About 1% of bariatric surgery patients die within a year of surgery, researchers here found, and the cumulative case fatality rate approaches 6% after five years.

DANVILLE, Pa. -- Losing between 5% and 10% of body weight before bariatric surgery improves outcomes for morbidly obese patients, researchers here said.

PHILADELPHIA -- Unexplained weight gain in patients with Crohn's disease treated with infliximab remains a mystery, according to investigators in a small study reported here.

IOWA CITY, Iowa -- A new picture of adenoviruses and the disease associated with them in the U.S. is emerging from a novel molecular technique, according to researchers here.

DURHAM, N.C. -- Oncologists need to think heart when treating early breast cancer, according to clinicians here.

BRISBANE, Australia -- Obesity even without reflux disease is associated with six times the risk of developing esophageal adenocarcinoma compared with those of normal weight, researchers here found.

BOSTON -- Women with high or rising blood pressure are up to three times more likely to develop diabetes, researchers here found.

CHARLOTTESVILLE, Va. -- Topiramate (Topamax), a migraine agent, appeared to help alcoholic patients curtail their heavy-drinking behavior, according to investigators here.

ST. LOUIS -- A maintenance program emphasizing behavioral or social skills may help overweight kids keep the pounds off after a weight loss intervention, researchers found.

BOURNEMOUTH, England-A campaign to urge kids to stop drinking sugared carbonated beverages-an effort to have them lose weight or prevent obesity-didn’t seem to have much value in the long run, reported investigators here.

LONDON -- Stormy relationships may increase long term wear and tear on the heart physically as well as emotionally, leading to a modestly increased risk of coronary events.

ROTTERDAM, The Netherlands -- Age-related macular degeneration appear linked with high baseline levels of C-reactive protein and associated inflammation, Dutch researchers found.

UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Adolescents don't get enough milk or calcium in their diets, and those who do consume dairy products tend to favor high-fat varieties, researchers found.

SAN DIEGO -- Once stereotyped as wasting away, HIV patients have joined the rest of America in fighting the battle of the bulge, according to results of a study reported here.

WACOL, Australia-Schizophrenia leads to an age-related mortality rate that is about 2.5 times that of the general population, and the difference appears to be increasing, researchers here reported.

WASHINGTON -- Computer giant Microsoft is surfing into the health-care information field with a free service that allows consumers to store their medical information online.

ST. LOUIS -- Pregnant obese women should gain less weight than currently recommended and women who are severely obese should actually lose weight during pregnancy, researchers here said.