
Urologists and pediatricians are puzzling over an apparent substantial increase in renal lithiasis among children.1 In 2007, a singlecenter study found a nearly 5-fold increase in the number of children presenting with kidney stones.

Urologists and pediatricians are puzzling over an apparent substantial increase in renal lithiasis among children.1 In 2007, a singlecenter study found a nearly 5-fold increase in the number of children presenting with kidney stones.

For 1 month, a 60-year-old white man has had increasing fatigue, generalized weakness, and exertional dyspnea. He becomes short of breath after he walks only 100 to 150 yards on level ground or climbs only 1 flight of stairs. In addition, he has unintentionally lost 12 lb in the past month and has experienced intermittent dysphagia with solid foods. He attributes this last symptom to long-standing gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), for which he regularly takes over-the-counter omeprazole.

For 3 months, a 43-year-old Bolivian woman had worsening thoracic and lumbar pain associated with tingling and tightness in the anterior upper and lower abdominal area, and numbness in the lower extremities. Her symptoms also included difficulty in walking (with frequent falls from imbalance), occasional urinary incontinence for the past few weeks, occasional afternoon low-grade fevers, and poor appetite with an associated 10-lb weight loss within the past 4 months.
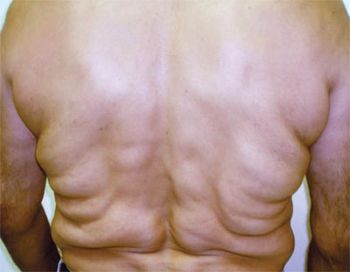
The multiple, symmetrically distributed, soft, nontender swellings on the shoulders and torso of a 56-year-old Hispanic man are characteristic of multiple symmetric lipomatosis (MSL), also known as Madelung disease or Launois- Bensaude syndrome.

I read with interest Dr Adam Breinig’s Practical Pointer, “For Easier Pap Smears, Use a Condom” (CONSULTANT, August 2009, page 488). I agree that this is an excellent way to retract the lateral vaginal walls during the speculum examination in an obese patient.

Body mass index (BMI) facilitates meaningful comparison of the weights of children of varying heights. It is useful in population studies, providing a measure of “fatness” that can be easily plotted and compared.
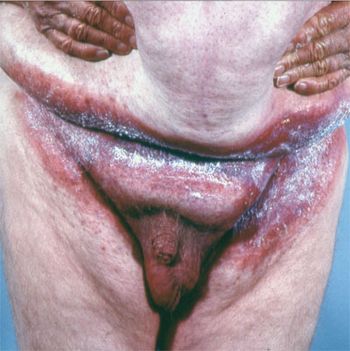
Case 4: An obese 59-year-old man presents with a chronic malodorous, itchy rash in his groin.

Nail lesions shown here: Onychogryphosis, pseudomonal infection, myxoid cyst, onycholisis.
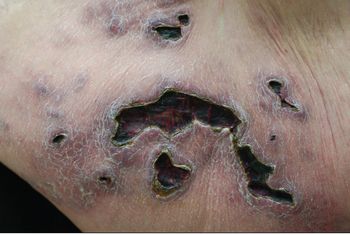
This abdominal rash developed while a 63-year-old woman was traveling in Israel. She was admitted to the hospital, where she received intravenous antibiotics, and was discharged after 5 days. She now returns to the United States and wonders what she had, because she did not understand what the physician in Israel had told her. She has brought all of her medical records.

I understand that patients with refractory hypertension have a high risk of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) syndrome. Can this be screened for in an office setting?

Case 1: Mr A. is a 55-year-old man who comes to your office for a routine physical examination. He is a traveling salesman and has recently gained weight. He does not exercise much and is a frequent visitor to fastfood establishments. His father had “a touch of diabetes” and died of a myocardial infarction (MI) at age 59.

No matter what primary care demographic your practice represents, it would be most unusual not to encounter patients infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV). Since HCV infection is chronic and can lead to cirrhosis (occurring in 20% of patients over a period of 10 to 20 years), decisions regarding its management, referral, and follow-up are of the utmost importance.

One of your patients is a 30-year-old woman whose BMI is 42. She has been treated for a compulsive eating disorder for the past 10 years, but medications and psychotherapy have not been effective.
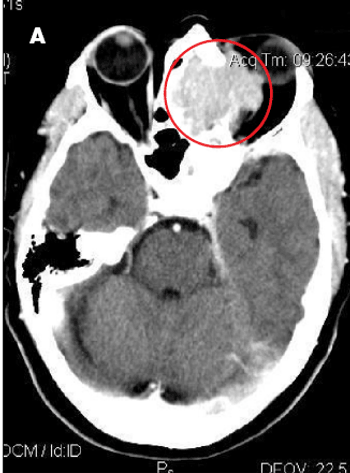
Progressively worsening nasal congestion and headaches with diplopia and left proptosis for 2 months prompted an ophthalmology consultation for a 67-year-old woman. She had been evaluated multiple times for allergic rhinitis and recurrent sinusitis.
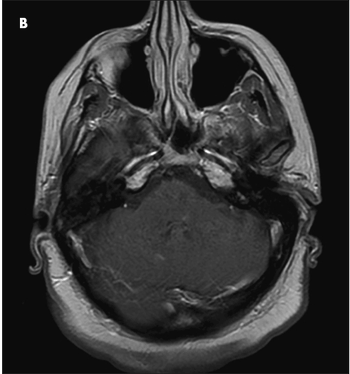
For a month, an obese 50-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertension had blurry vision in both eyes. During this time, she also had ataxia and right-sided numbness. For the past 2 days, she had had horizontal, binocular diplopia with right gaze.

I have been using the finger of a non-sterile glove

Performing Papanicolaou tests in obese patients can be difficult

Unilateral polythelia is suggested by a sequence of supernumerary nipples that follow the embryonic milk line. No areolae are associated with these accessory nipples.

In 2000, the World Allergy Organization (WAO) published a consensus definition of anaphylaxis as a severe, life-threatening generalized or systemic hypersensitivity reaction. The reaction is caused by the release of bioactive mediators from mast cells and basophils.

All elements of the skin are affected by age. In this 2-part article, I discuss how the blood vessels, the lymphatics, and the ground substance- which surrounds these vessels- respond to age, and I show how the aging elements of the vasculature can engender a variety of pathological cutaneous conditions.

Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the injury, and a level of disability at the time of the injury and shortly after.
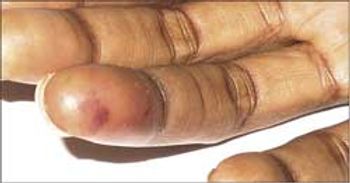
Osler nodes may accompany bacteremia without endocarditis, septic endarteritis, typhoid fever, gonococcemia, systemic lupus erythematosus, and nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis.
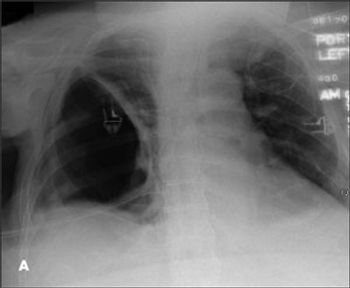
For 3 months, a 63-year-old man had experienced progressively worsening dyspnea. He denied fever, weight loss, and hemoptysis. Eight months earlier, he had had a right thoracotomy to drain a right empyema. Comorbidities included morbid obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and obstructive sleep apnea. However, he did not have any intrinsic lung disease.
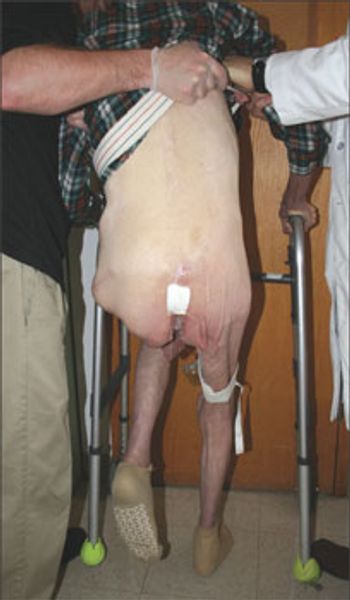
An 88-year-old man who had left hip repair after a fracture a few months earlier is now admitted to behavioral hospital because of implacable refusal to take medications, and because of poor food intake and ongoing refusal of rehabilitation. Ambulated with a walker before fracture but now barely ventures out of wheelchair even with rolling walker and therapist guidance.

Losing weight can significantly reduce intracranial pressure and the complications it causes, including headache and optic nerve anomalies.