
To what do you attribute symptoms of rash and fever in: a man with type 2 diabetes; a woman with systemic lupus erythematosus; a previously healthy girl.

To what do you attribute symptoms of rash and fever in: a man with type 2 diabetes; a woman with systemic lupus erythematosus; a previously healthy girl.

An 82-year-old man presents with shoulder pain resulting from a fall the day before. He has had intermittent episodes of light-headedness, chest pain, and "flutterings in the chest" over the past week--including one this morning. Episodes last about 2 hours and resolve spontaneously. He denies any loss of consciousness, weakness, or worsening of symptoms with exertion. He also denies headache, abdominal pain, and other injuries. His medical history includes coronary artery disease (treated with bypass grafting 10 years earlier); prostate cancer; and chronic lymphocytic leukemia, for which he is receiving chemotherapy.

An 82-year-old man presents with shoulder pain resulting from a fall the day before. He has had intermittent episodes of light-headedness, chest pain, and "flutterings in the chest" over the past week--including one this morning.

Three case studies of patients with fever and rash challenge you to distinguish infectious from other causes and serious from non-threatening.

DALLAS -- Myocardial infarction survivors who have ventricular dysfunction as measured by an ejection fraction of less than 40% should receive implantable cardioverter defibrillators to prevent sudden cardiac death.

ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- When the cumulative bill for ischemic stroke comes due in 2050 it is likely to total .2 trillion, and that's a conservative estimate, calculated University of Michigan researchers.

HOUSTON -- The cardiotoxicity levels of two effective approaches to breast cancer, Herceptin (trastuzumab) for HER2-positive disease and radiation to the left breast, have been newly quantified.

An update on developments in infective endocarditis by addressing a number of questions physicians commonly raise concerning prophylaxis, diagnosis, and management.

DALLAS -- For patients with cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease is often a fellow traveler, necessitating more sensitive diagnostic tools than serum creatinine alone.

SAN FRANCISCO -- Even though anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation may boost the chance of an intracranial bleed slightly in older patients, the benefits of the therapy outweigh the risk of a hemorrhage, according to researchers here.

PAMPLONA, Spain -- Severe obstructive sleep apnea more than doubled the risk of a first ischemic stroke in persons over age 70, researchers here reported.

NEW YORK -- Stroke risk trumps age, gender or other history of heart disease in determining which atrial fibrillation patients benefit from anticoagulation, according to revised guidelines issued today by the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, and the European Society of Cardiology.

We describe a case in which a patient received thrombolytic therapy after he presented with a clinical picture consistent with submassive pulmonary embolism (PE). Two months later, a malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor was diagnosed, and the patient died with metastatic disease. The filling defect in the left main pulmonary artery originally interpreted as PE was in fact a tumor. This case describes an unusual presentation of a rare disease (malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor) mimicking a submassive PE.

A middle-aged woman is experiencing episodes of chest pain and fatigue. Although stress test results are positive for ischemia, coronary angiography reveals open arteries. What next step would you take?

An 81-year-old Asian woman was at a family function when she briefly complained of a severe headache, then quickly lost consciousness. She was brought to the hospital within 2 hours of symptom onset.

Is the weight gain associated with thiazolidinediones (TZDs) counterproductive to the treatment of diabetes?

A succinct review of hyperkalemia . . . its various causes, clinical manifestations and consequences, ECG findings, and treatment approaches.

ADELAIDE, Australia -- Men appear to have a 50% higher risk than women of recurrent venous thromboembolism after stopping anticoagulant treatment, researchers here reported.

PHILADELPHIA -- Gleevec (imatinib), the major prominent symbol of the age of targeted anti-cancer drugs, can on occasion cause serious cardiotoxicity with congestive heart failure, according to researchers.

GRONINGEN, The Netherlands -- Two decades after they were treated with Adriamycin (doxorubicin) for osteogenic sarcoma or malignant fibrous histiocytoma, the cardiac status of 22 long-term survivors continues to worsen.

ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Although the prevalence of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction has increased, survival rates for these patients with diastolic heart failure remain similar to those with a reduced ejection fraction, according to two studies.
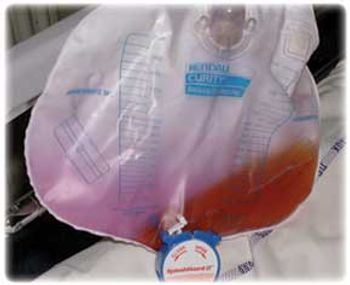
A staff nurse calls the physician to see "something really bizarre-we have no idea what this is": the plastic of a urine collection bag of an 81-year-old woman has turned purple, although the urine within is more orange-brown and distinctly less odd looking. Patient has had an indwelling urethral catheter for 7 months, and this discoloration had not been noted before. Current history includes marked constipation, atrial fibrillation, and symptomatic osteoarthrosis of the hips and knees.

ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Repair of a faulty mitral valve is worth the risk regardless of patient age, even though it has been considered a perilous procedure, according to researchers here.

BOSTON -- Protection against congestive heart failure (CHF) by moderate drinking appears to be conferred by a previously unsuspected mechanism, according to researchers here.

FRAMINGHAM, Mass. -- Children of parents who develop heart failure appear to be predisposed themselves to both left-ventricular systolic dysfunction and overt heart failure, researchers here reported.