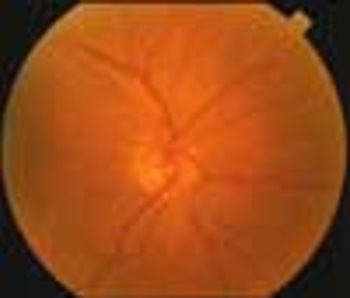
You have been treating a 28-year-old woman for migraine for the past 4 years. This morning, after reading the headlines about the potential risks of mixing triptans with triptans , she calls your office to ask whether she should stop taking her antidepressant.