
They work all week at stressful jobs without a headache--and spend the weekend in bed with a breakthrough migraine. What to do for them?

They work all week at stressful jobs without a headache--and spend the weekend in bed with a breakthrough migraine. What to do for them?

Do you know what drugs current guidelines recommend? Get an 8-slide update, here.

If one triptan doesn't work for your patient's migraines, try, try again. A neurologist offers tips on the pros and cons of the 6 available agents.

What it all boils down to: smoking is a risk factor for stroke--no matter your age or your migraine status.

By asking and answering these questions, I learned some new tricks that can help you help migraine sufferers.
What brings patients to your office-and not the specialty office down the street? Insights in this slideshow.

Triptan and ergotamine drugs are staples of acute migraine treatment. But questions about their cardiovascular safety linger in the absence of clear evidence. A short slide show looks at what we do know.

This benign, solitary, nodular tumor on the lower eyelid arises from the follicular infundibulum. What do you know about this condition and the 4 others in this quiz?

Better understanding of migraine causes and related issues could result in enhanced patient care and prevention, but clinicians face some serious challenges-here are 5.
Researchers are finding some useful answers about migraine treatment and prevention.

When is a headache more than just a headache? How best to treat a corneal ulcer? When can a patient with asthma safely undergo elective surgery? Here: tips to help you prepare for your recertification exam-and to help you in your daily practice.

In the news: respiratory disease underdiagnosed, Alzheimer biomarkers, Crohn disease microbiome, migraine device, sleep apnea and diabetes.

In the news: stroke prevention, heart disease and women, migraine and depression, cholinesterase inhibitors and dementia, multivitamins and cataract risk.

Chronic pain affects more Americans than diabetes mellitus, heart disease, and cancer combined. Here are some facts and figures about pain for you to consider.
Neurological disorders have been considered a significant threat to public health for some time. Take a look at these facts and figures.

The current study may help create new pathways for better understanding and developing more effective and more specific medications.

Most patients have a sophisticated idea of what causes their headaches, but the chances of this information being wrong are higher than desirable unless the patient formally experimented with triggers.

This condition is a more important risk factor than previously thought and should not be taken lightly.
Stroke survival and thoughts of suicide; PCP shortage; pediatric headache treatments; antidepressants and prolonged QT interval; calcium supplements, men, and CVD.

Topiramate and trazadone showed only limited efficacy in pediatric headache. For flunarizine, pizotifen, propranolol, and valproate, no evidence was found to support their use.

Stigma correlated most strongly with inability to work and was greater for chronic migraine than for epilepsy or episodic migraine.
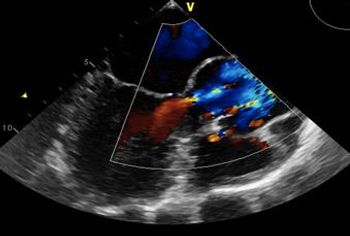
PFO can be detected in 10% to 15% of the population by transthoracic echocardiogram. Autopsy studies show a prevalence of PFO of approximately 26%.
FDA Approves New Flu Vaccine: Drug Trio Increases Kidney Risk; Spotting Problem Drinkers; Migraines and Blood Clots; New Class of Diabetes Drug

Medication is seldom necessary. Education is the key element of therapy. An explanation of the process and a discussion of possible triggers-lack of sleep, stress, missed meals etc-is the most key intervention.

School performance is more likely to be below average in children who have migraine than in those who do not have headaches.