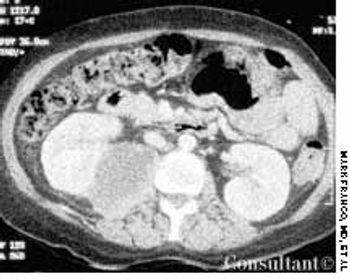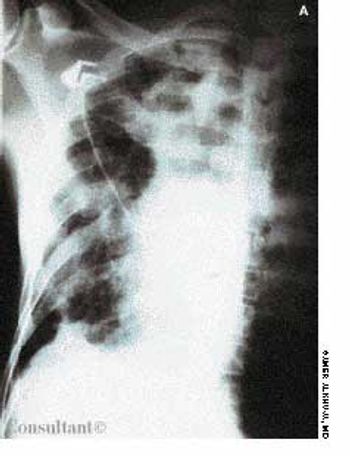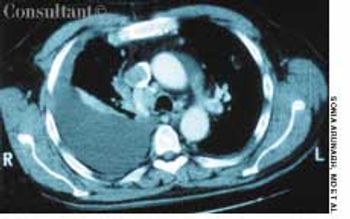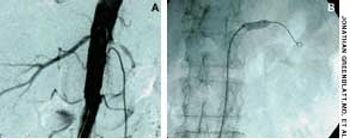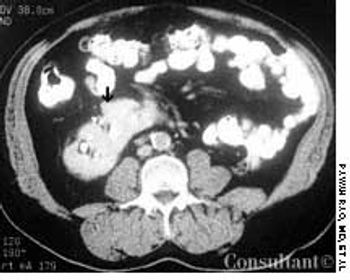
Frequent urinary tract infections and unexplained hypertension (160/100 mm Hg) occurred in a 38-year-old man with no significant medical history. The heart and chest were normal; a right lower quadrant mass was detected in the abdomen. Red blood cells were found in the urine. An abdominal CT scan demonstrated that the left kidney was fused to the lower pole of the right kidney with the left pelvicaliceal system to the left of the midline; these findings are consistent with crossed fused renal ectopia. Cystographic and cystoscopic examinations were normal.