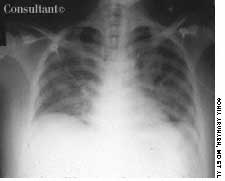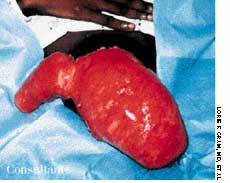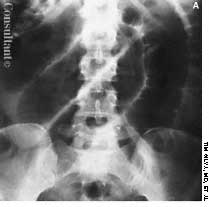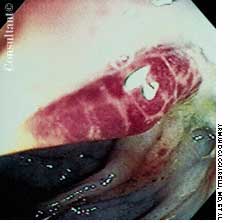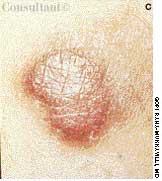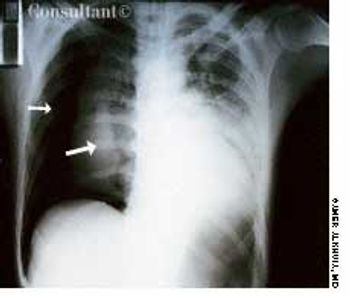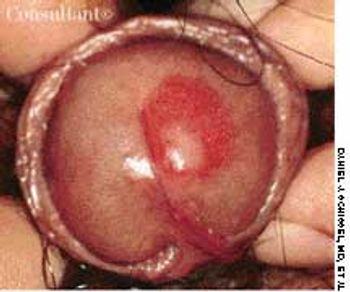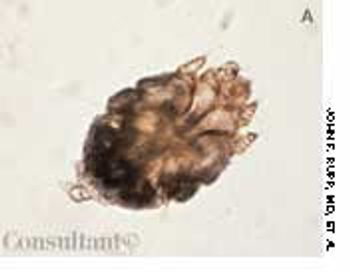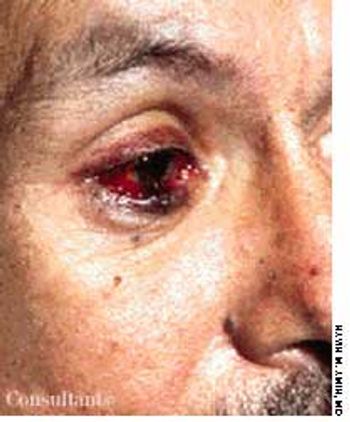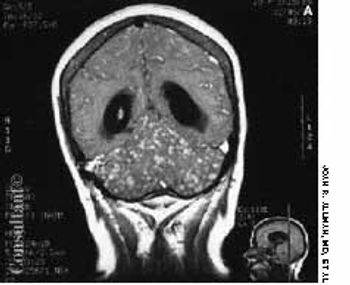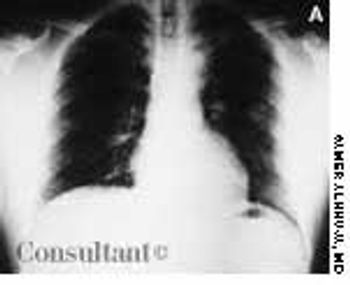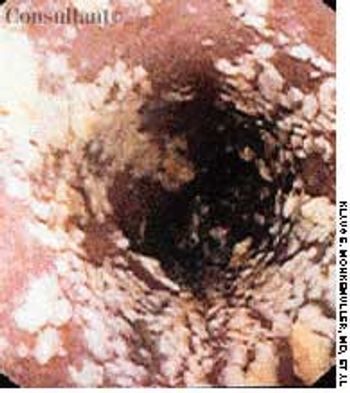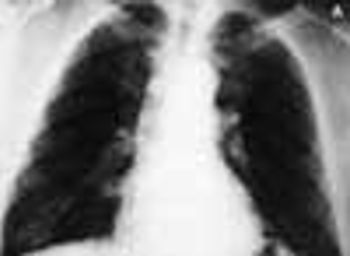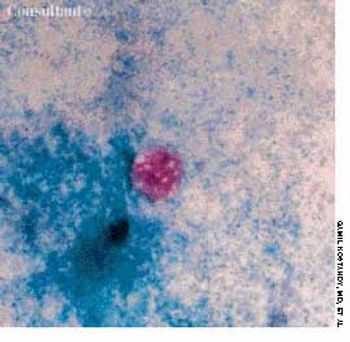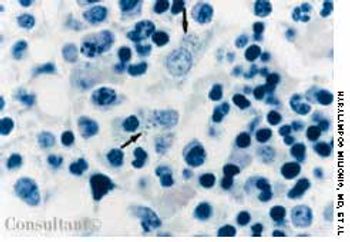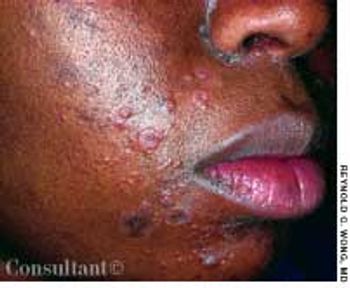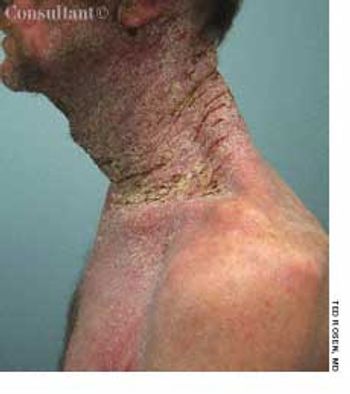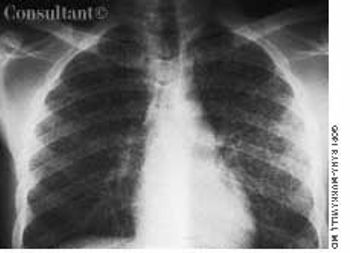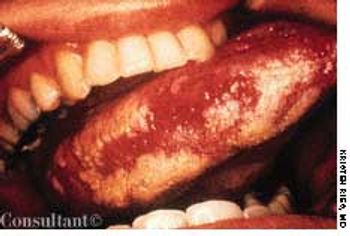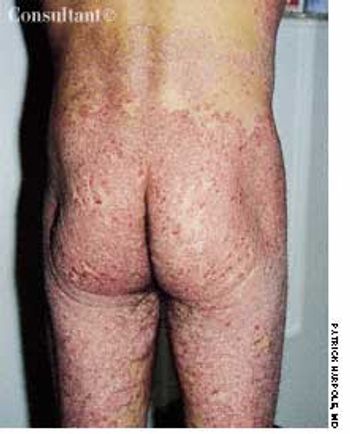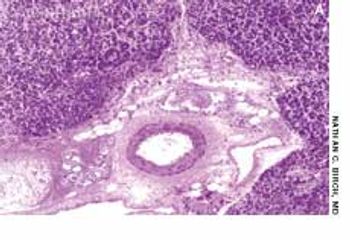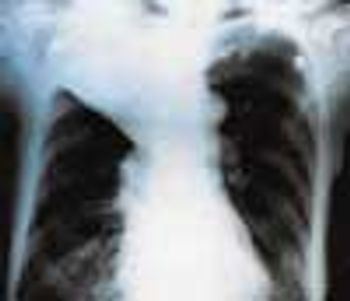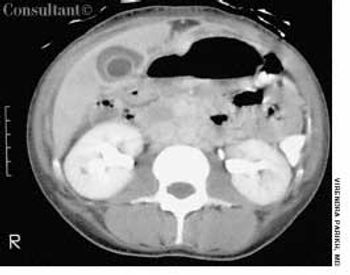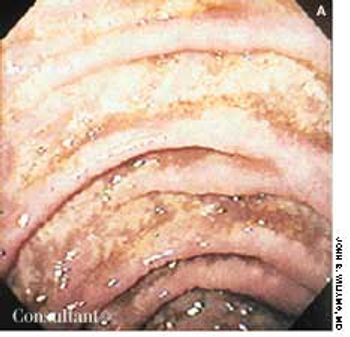
A 33-year-old man with AIDS presented to the emergency department with fever, dyspnea, cough, and pleuritic chest pain of 3 days' duration. He had had a Pneumocystis carinii infection 3 years before recently emigrating from the Dominican Republic to the United States. Promiscuous sexual activity was his only risk factor for HIV infection. The patient did not take antiretroviral medications or protease inhibitors because of their cost.