
Here's a look at some of the ways people have been dying lately -- from the common to the unusual.

Here's a look at some of the ways people have been dying lately -- from the common to the unusual.
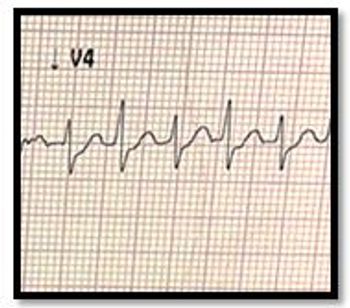
Fifty-year-old female w/ HTN, DM seen in ED for palpitations, near-syncope. Weak rapid pulse (210 bpm), BP 75/35 mmHg. What's your ECG read?


Myosis is accompanied by acute onset dizziness, double vision, and asthenia. What's in your differential diagnosis?
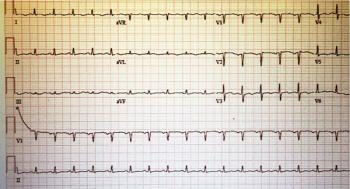
What does the office-based ECG tell you about the patient's complaint of recently worsening asthenia and dyspnea?

COPD… nasal polyps.. gout …. dyskinesia in Parkinson Disease: here’s a brief look at new drugs for these and other disorders coming your way.
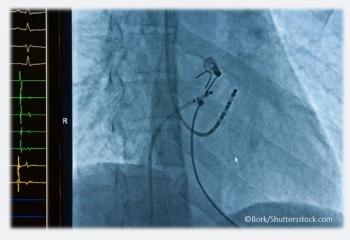
That depends, as suggested by results of the CASTLE-AF study, presented at ESC Congress 2017, in Barcelona, Spain.
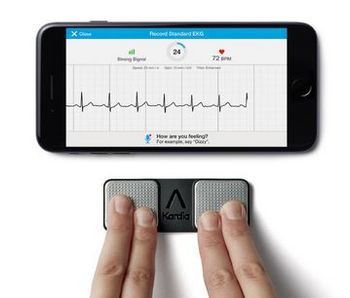
Diagnosis of atrial fibrillation via handheld iECG monitor looks promising but can we pay for it yet?

A small study raises big questions about patients' perceptions of AF symptoms after pulmonary vein ablation. What do you think?

Increased detection of subclinical atrial fibrillation intensifies a common clinical quandary in AF patients: to anticoagulate, or not?

A new study found an increase in diet-quality scores over 12 years was linked to an 8%-17% reduction in mortality.
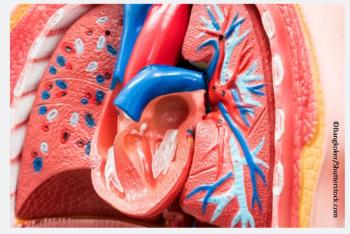
The link between early asthma and left ventricular hypertrophy was independent of a range of major cardiovascular risk factors.
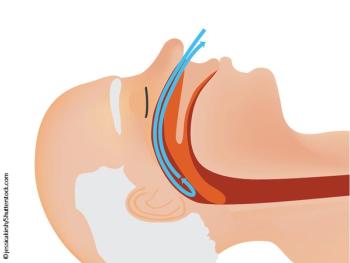
Some find new meta-analysis results disturbing; others say they underscore the need for more focused research.


The answer, and the evidence behind it, are essential knowledge for primary care.
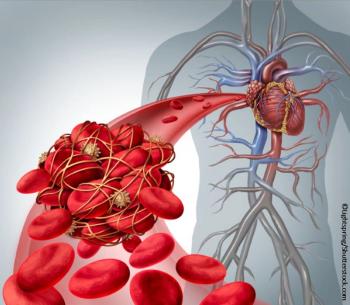
Rhythm vs rate control and which medication(s) for which patients, when, and why? Test yourself.

Medicine is finally catching up with the smartphone/smartwatch era – and it’s about time!
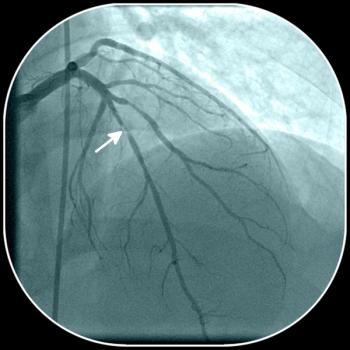
Antiretroviral drug regimens have been implicated as factors in the increased risk of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction in those with HIV infection. Here: practical measures for prevention and screening.

In the context of metabolic syndrome, sleep is thought to be an added and modifiable risk factor.

A1C vs FPG to diagnose prediabetes; prediabetes and CHF; and how much weight loss is too much? Reports from ADA 2017.

Does coffee increase AF risk? How about chocolate? Marijuana? Test yourself with our quiz so you can counsel your patients.
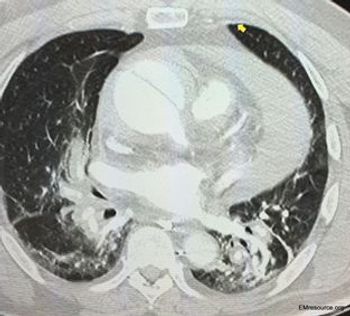
The patient with hypertension and syncope had cardiac tamponade. Causes, symptoms, and treatment described here.
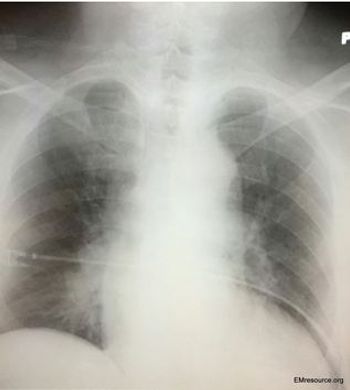
A man with a history of hypertension had syncope and felt “sweaty.” Chest x-ray was normal. What’s your next test?
Heme iron, nitrites, and nitrates are implicated in the largest study to date to show increased mortality risks linked to eating red meat.
