
SOUTHAMPTON, England -- Smarter kids are more likely to adopt limited vegetarianism when they mature, according to a large British cohort study.

SOUTHAMPTON, England -- Smarter kids are more likely to adopt limited vegetarianism when they mature, according to a large British cohort study.

TORONTO -- For patients with fluid-retaining conditions, the simple act of lying down in bed at night may cause a fluid shift to the upper body that results in obstructive sleep apnea, a small study here suggested.

TORONTO -- For patients with fluid-retaining conditions, the simple act of lying down in bed at night may cause a fluid shift to the upper body that results in obstructive sleep apnea, a small study here suggested.

SAN ANTONIO -- A diet with 20% of calories from fat, or less, may help reduce risk of breast cancer recurrence, particularly for women with hormone-receptor negative disease, according to a large trial.

SAN ANTONIO -- A diet with 20% of calories from fat, or less, may help reduce risk of breast cancer recurrence, particularly for women with hormone-receptor negative disease, according to a large trial.

NASHVILLE, Tenn.-- Avastin (bevacizumab) added to chemotherapy for non-squamous cell, non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) increased survival by two months, but treatment-related deaths rose.

NASHVILLE, Tenn.-- Avastin (bevacizumab) added to chemotherapy for non-squamous cell, non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) increased survival by two months, but treatment-related deaths rose.

ST. LOUIS, Dec. 12 -- Exercise can counteract the bone-mineral density loss that is triggered by calorie restriction, according to a small study.

LONDON -- Men who lose three centimeters or more of height (about 1.18 inches) as they age are at increased risk of death, compared with men who lose less than a centimeter, according to a longitudinal study here.

ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Smoking accelerates cartilage loss and increases pain in men with knee osteoarthritis, researchers here reported.

ST. LOUIS -- Long-term lifestyle modifications, particularly cutting way back on the consumption of protein, seems to be associated with reduced levels of markers of cancer risk, researchers here said.

NEW YORK -- The action by this city's Board of Health to ban the use of artificial trans fats in restaurants, ranging from pizzerias and delis to bakeries and upscale restaurants, could have fallout for mouths and lipid levels across the nation.

MINNETONKA, Minn. -- The healthiest state in the nation appears to be Minnesota, land of Wobegon and 10,000 other lakes, low cardiovascular death rates, and a well-insured population, according to the United Health Foundation here.

A 71-year-old man presents with a2-week history of early satiety, decreasedappetite, postprandial nauseaand vomiting, jaundice, dark urine,acholic stools, and generalized pruritus.In addition, he reports a 4.5-kg(10-lb) weight loss within the past2 months.

A 52-year-old man presented to his primary care physician with shortness of breath for 5 days, right-sided lower thoracic back pain, and dry cough. The patient was a 15-pack-year cigarette smoker who had emigrated from China to the United States in 1989. He had no significant history of occupational exposure or tuberculosis. He had no significant weight loss, and his past medical history was otherwise unremarkable.
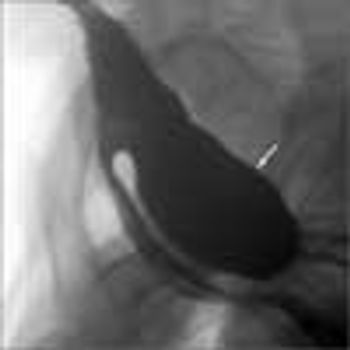
A 72-year-old man was evaluated for worsening dysphagia and weight loss. The dysphagia had been intermittent for 20 years, but in the past year it had begun to occur daily. He regurgitated food after every meal, often many hours after ingestion.
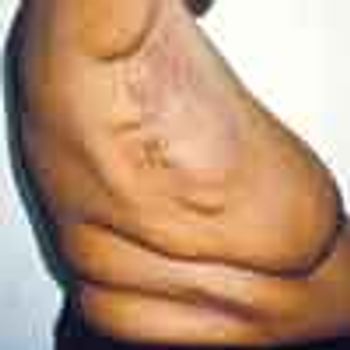
For years, a 46-year-old African American woman had had progressive weight gain (despite a low-calorie diet), fatigue, and severe muscle cramps. On examination, Mandeep Hundal, MD, Rashid Khan, MD, Rajeev Garg, MD, and Niraj Mehta, MD, of the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, noted symmetrically distributed fatty lumps in the patient's neck, axillary and mammary regions, and proximal segments of the arms and legs. These findings are characteristic of Madelung disease, which is also known as multiple symmetric lipomatosis (MSL) or Launois-Bensaude syndrome.

BALTIMORE -- A poor childhood more than doubles the risk of early heart disease even among white male physicians who achieve a high socioeconomic status, found researchers here.

LEXINGTON, Ky. -- Yo-yo weight loss may increase the risk of gallstone disease in men, researchers reported.

BOSTON -- Cross ovulation and menstrual cycle patterns off the list for an explanation of why overweight women have less of a risk for premenopausal breast cancer, says a Harvard group. Instead, think hormonal for the perplexing protective effect.

DALLAS -- Weight-loss surgery may be too risky for older patients, according to a population-based study of outcomes.

SAN DIEGO -- High blood pressure during pregnancy may be a warning sign for stroke or other cardiovascular events later in life, reported researchers here.

WASHINGTON -- For overweight patients with osteoarthritis of the knee, even a relatively minor weight loss can make a significant long-term difference in improving quality of life, a researcher said here.

CHICAGO -- In a head-to-head trial with the sulfonylurea Amaryl (glimepiride), Actos (pioglitazone), a thiazolidinedione, appeared to slow the progression of a marker for atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes, researchers reported here.

PHILADELPHIA -- When a patient with an orthopedic implant develops a rash or inflammatory symptoms, think metal allergy, suggested researchers here.