
When a patient presents with unilateral abdominal pain, always consider shingles--especially if the patient is elderly.

When a patient presents with unilateral abdominal pain, always consider shingles--especially if the patient is elderly.

A 39-year-old woman has a tender vesicular rash on her finger. A similar rash that had appeared on the same finger 1 year earlier responded slowly to a course of oral cephalexin

ABSTRACT: Although the widespread use of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing has led to an increase in the number of cancers detected, controversies about the benefits of screening persist. No conclusive evidence has yet emerged that PSA screening reduces the mortality associated with prostate cancer. Thus, mass screening is not universally endorsed. The American Urologic Association and the American Cancer Society recommend that digital rectal examination and PSA testing be offered annually to men 50 years and older with an estimated life expec- tancy of 10 years or more. High-risk patients (those with a positive family history or those of African American descent) are advised to begin screening at age 45. The decision to screen is based on the patient's preference following a thorough discussion of the benefits and limitations of PSA testing. Refer to a urologist any patient with a PSA greater than 4.0 ng/mL. Also, be alert for high PSA velocity changes in patients undergoing annual screening, and refer those with a PSA velocity of more than 0.75 ng/mL/y.
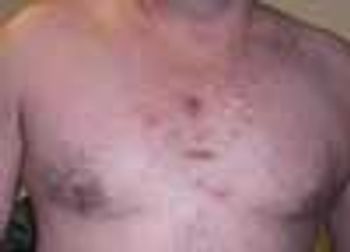
Painful cysts on the sternal and left axillary regions that had worsened over the past 3 weeks prompted a 42-year-old man to seek medical care. He reported that similar lesions in the same distribution first arose when he was 25 years old, and they recur each year. He denied having cystic acne in adolescence.
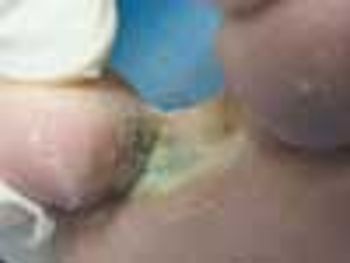
For a year, a 31-year-old man had asymptomatic, malodorous discoloration of the toe web spaces. He stated that his feet perspire heavily in the boots he is required to wear for work.

A 23-year-old man presents to theemergency department (ED) withacute chest discomfort, which startedin the morning. He describes the discomfortas more akin to palpitationsthan to actual pain. The discomfortis midsternal, nonradiating, nonpleuritic,and associated with dyspnea; itis neither exertional nor positional.There is no viral prodrome.

These painful eczematous lesionsat the angle of the mouth and thebase of the nostrils had been presentin a 52-year-old woman for 3days (A). Some of the vesicles hadulcerated and left a crust over theregion. The patient said she had hadsimilar attacks in the past. The diagnosisof recurrent herpes simplexvirus 1 (HSV-1) infection was made.The patient was treated with acyclovirfor 1 week, and all the lesionsdisappeared.

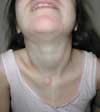
An 18-year-old man presented with a 3-day history of fever, sore throat, and neck swelling. He had previously been healthy, and his immunizations were up-to-date. There was no history of travel outside the country or of an animal bite or scratch.

For a year, a 31-year-old man had asymptomatic, malodorous discoloration of the toe web spaces. He stated that his feet perspire heavily in the boots he is required to wear for work.

Painful cysts on the sternal and left axillary regions that had worsened over the past 3 weeks prompted a 42-year-old man to seek medical care. He reported that similar lesions in the same distribution first arose when he was 25 years old, and they recur each year. He denied having cystic acne in adolescence.

When you suspect blunt nerve trauma, referral to a hand surgeon is prudent-even without evidence of acute compartment syndrome. The same is true if you discover ischemia in any part of the hand after injury. Try to control hemorrhage with compression and elevation of the involved extremity. If this is unsuccessful, use a short-duration tourniquet. Do not attempt to clamp a bleeding vessel; the risk of causing serious nerve or tendon damage is too high. Avoid exploring wounds in the region distal to the midpalmar crease and proximal to the proximal interphalangeal flexor crease because of the high risk of damaging the flexor tendons and the annular ligaments in this region. Explore more proximal injuries cautiously to determine occult injury to the flexor tendon.

ABSTRACT: To determine the stability of the injury, examine phalangeal and metacarpal fractures for intra-articular involvement. Suspect carpal bone fracture in any patient with wrist pain and tenderness; proper splinting is essential to prevent avascular necrosis of the bone, arthritis, and chronic disability. After successful reduction of a distal or proximal interphalangeal joint dislocation, order follow-up x-ray films. Apply stress testing of the joint space to all injured joints to ensure ligamentous integrity. Carpal and carpometacarpal dislocations require immediate consultation with a hand specialist. Therapy for bite wounds includes copious irrigation, debridement (in the operating room if necessary), and antibiotic prophylaxis. A patient with an infected bite wound requires hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics.

Appropriate foot care, preventive measures, and early intervention reduce the incidence of complications and lower extremity amputation in patients with diabetic foot ulcers. A thorough lower extremity examination includes assessment of the skin, interdigital areas, skin quality and integrity, and ulcerative or pre-ulcerative changes. The key to prevention is patient education and lifelong commitment to self-care.

A 65-year-old woman presented withdouble vision of 2 days’ duration.The diplopia mainly occurred whenshe looked toward her right. She deniednausea, vomiting, vision loss,headache, change in mental status,facial pain, weakness in the extremities,and sinus infection. She had nohistory of head trauma or systemicmalignancy.
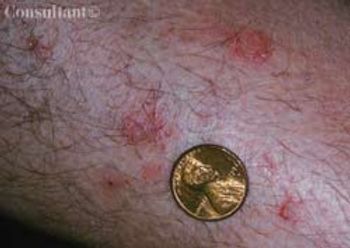
The multiple, uniformly scaly, coin-shaped, papulosquamous lesions shown here on the lower leg of a 61-year-old man had persisted for 3 months despite application of topical clotrimazole and 1% hydrocortisone. The rash involved only the legs and was variably pruritic. The patient had a long history of dry skin.
A 58-year-old man with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension was hospitalized with acute diarrhea characterized by several brown, liquid depositions per day. He also complained of lower abdominal pain and bloating and a 10-lb weight loss in the past 2 months. He denied fever or chills, use of corticosteroids, and travel outside the United States.

Unrelated abnormalities in the preauricular area were noted in a 50-year-old man who had presented with acute rhinosinusitis following an upper respiratory tract infection. The patient stated that he had had these deformities since birth.
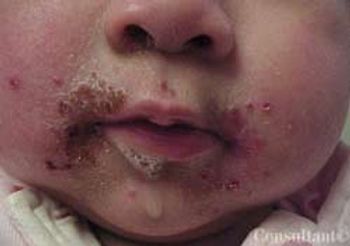
For 3 days, a 5-month-old infant had a red, papular, nonpruritic rash around her mouth and vesicles on her hands. The child was being breast-fed by her mother, who had a similar rash around her nipple. The child was afebrile, and the physical examination revealed no abnormal findings. There was no history of allergy or change in diet.

ABSTRACT: Rely on the history and physical findings when you evaluate a hand injury. After you control any active bleeding, test the motor and sensory functions of the radial, ulnar, and medial nerves. Use the rule of the 5 P's-pulses, pallor, pain, paresthesia, and paralysis-to guide the vascular examination. Assess the muscles and tendons by testing their flexion and extension functions against mild resistance. After anesthetizing any wound sites, apply high-pressure saline irrigation to remove debris and reduce bacterial contamination to prevent infection. To repair skin injuries, use a closure method appropriate to the condition of the wound. Infection-prone wounds-such as crush, grossly contaminated, and bite injuries-may require antibiotic prophylaxis and possibly delayed closure.

ABSTRACT: Occult bacteremia now occurs in only 1 of 200 children who present with acute fever (temperature of 39°C [102.2°F] or higher) and white blood cell counts of 15,000/µL or more. The most likely cause of bacteremia remains Streptococcus pneumoniae; when there is no evidence of toxicity, such bacteremia is generally a benign, self-limited event. Because of the extremely low yield, blood cultures are no longer routinely warranted in children aged 3 to 36 months who have no obvious source of infection, and empiric treatment of occult bacteremia is no longer appropriate. Almost all cases will spontaneously resolve with a low rate of subsequent focal infection. If a child remains febrile and worsens clinically, further diagnostic evaluation and possible empiric treatment with antibiotics pending results of cultures may be considered.

ABSTRACT: The rate at which acute dyspnea develops can point to its cause. A sudden onset strongly suggests pneumothorax (especially in a young, otherwise healthy patient) or pulmonary embolism (particularly in an immobilized patient). More gradual development of breathlessness indicates pulmonary infection, asthma, pulmonary edema, or neurologic or muscular disease. A chest film best identifies the cause of acute dyspnea; it can reveal pneumothorax, infiltrates, and edema. Pulmonary embolism is suggested by a sudden exacerbation of dyspnea, increased ventilation, and a drop in PaCO2. A normal chest radiograph reinforces the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism, which can frequently be confirmed by a spiral CT scan of the chest. Pneumonia can be difficult to distinguish from pulmonary edema. In this setting, bronchoalveolar lavage and identification of the infectious organism may be necessary to differentiate between the 2 disorders.

A 51-year-old patient asked me whether she should receive the influenza vaccine. She was last vaccinated in 1976; symptoms that resemble Guillain-Barré syndrome developed shortly afterwards. She has not received the vaccine since then; however, because she teaches schoolchildren, she wondered whether she should be vaccinated.

For several months, a 59-year-oldwoman has had numerous asymptomaticlesions on her arms andlegs. During this period, she has notbeen exposed to the sun and hastaken no new medications.

A 72-year-old woman first noticed progressive enlargement of the maxillary area of her face 18 years earlier. She denied facial trauma and significant dental caries. Her medical history consisted of breast cancer managed by a mastectomy and type 2 diabetes mellitus of 3 years’ duration.

ABSTRACT: A host of evidence supports the treatment of high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins), which are effective in both primary and secondary prevention of coronary heart disease (CHD). Studies have shown that statins prevent first cardiac events in otherwise healthy persons with elevated LDL cholesterol and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. Statins are also associated with a reduction in cardiac death, stroke, hospitalization, and the need for revascularization in patients with established CHD and hyperlipidemia. Secondary prevention trials of statin therapy that included persons aged 65 to 75 years found significant risk reduction in this age group. Among the concerns associated with statin treatment are lack of proper titration, failure to achieve LDL target goals, and underuse in patients with established CHD.