
An important study demonstrated the efficacy of chlorthalidone for the treatmentof systolic hypertension in elderly persons,1 and the results have been validatedby other studies.

An important study demonstrated the efficacy of chlorthalidone for the treatmentof systolic hypertension in elderly persons,1 and the results have been validatedby other studies.

At what blood pressure is it prudent to treat newly diagnosed hypertension with 2 antihypertensive agents, and what criteria should guide selection of the 2 drugs?

Under what circumstances is it worthwhile to measure aldosterone levels in hypertensive patients? An increasing number of cardiovascular risk factors are being packaged into individual "epidemics."

I encourage my patients to use the blood pressure machines found in most pharmacies, but I often find that the readings seem significantly lower than those I obtain in my office using a standard mercury sphygmomanometer.

As many as 10% of Americans older than 20 years have type 2 diabetes, and more than 20% of the total population has the metabolic syndrome. Type 2 diabetes will develop in many of those with the metabolic syndrome.

Systolic hypertension is an independent risk factor for coronary artery disease, stroke, and end-stage renal disease. Nonpharmacological interventions for systolic hypertension include limitation of dietary sodium and alcohol intake along with weight reduction and aerobic exercise.

An 84-year-old woman with progressive stenosis of the cervical spinal canal, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, hypertension, and stable angina presents to her primary care physician after an appointment with the orthopedist who is monitoring her chronic degenerative joint disease.
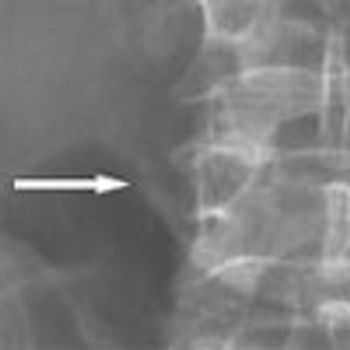
An obese 61-year-old man with a history of heroin abuse was brought to the hospital after he had fallen onto his buttocks on a sidewalk. He was able to stand initially, but weakness and numb-ness in his legs rendered him suddenly unable to walk or prevent himself from voiding. He denied abdominal or back pain. His medical history included asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and hypertension.

To help answer the question of Mary Ellen Lewis, PA-C, about her patient with a low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol level of 120 mg/dL and a high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol level of 100 mg/dL(CONSULTANT, June 2007), I would like to describe my approach to the treatment of dyslipidemia.

A 62-year-old man presents with painful cramps in his left lower leg that began about 6 months earlier and have recently become more frequent. The cramps occur with vigorous walking and cease when he stops for several minutes.

Nephropathy develops in about 30% of patients with diabetes. Screen for albuminuria at the time type 2 diabetes is diagnosed and within 5 years of diagnosis of type 1 diabetes.

An oral renin inhibitor, aliskiren, recently became available. Does it have any advantages over angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)?

When angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors were first discovered, they were a welcome addition to the antihypertensive armamentarium. Since then, many more benefits of these drugs have been found: they slow the progression of diabetic nephropathy, abate the sequelae of heart failure when systolic dysfunction is present, and reduce the level of proteinuria in patients with nephrotic syndrome.
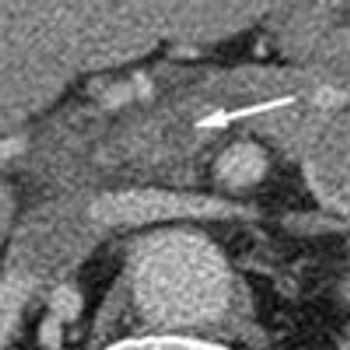
Acute abdominal pain, fever, and chills prompted a 51-year-old man to visit his local hospital twice in one week. On both visits, a clinical and laboratory workup was negative. He then presented to a tertiary care center with worsening symptoms. His history included hypertension and tobacco and alcohol use.

Some of my patients who are being treated for hypertension, hyperlipidemia, or both claim that an elevated blood pressure reading or lipid level measurement resulted from a sodium- or fat-laden meal that they had eaten 1 or 2 days before their office visit.

At what level should a patient's blood pressure be before he or she has carotid surgery?

Treatment of hypertension can minimize both microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes and helps prevent nephropathy and cardiovascular events.
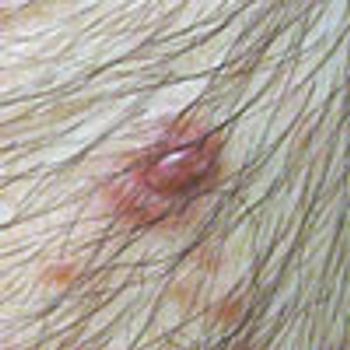
The red, 1- to 3-mm lesions on the right forearm of a 19-year-old man had recently become tender after being asymptomatic for 10 years. The patient described a shooting pain on palpation. Previous biopsy results showed no cancer. He had high blood pressure but was otherwise healthy. His father had similar lesions.
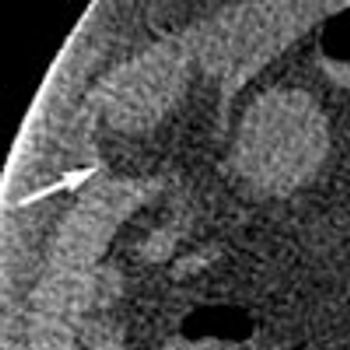
A 50-year-old man with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension presented to the emergency department with abdominal pain and vomiting of 2 days' duration. He denied fever and urinary symptoms.

An 81-year-old woman with a history of moderate Alzheimer dementia, depression, coronary artery disease, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes mellitus was accompanied to the office by her son for a routine follow-up appointment.

BOSTON -- Women with high or rising blood pressure are up to three times more likely to develop diabetes, researchers here found.

BOSTON -- Patients enrolled in Medicaid managed care plans are less likely to achieve good blood pressure control, receive breast cancer screening, or have timely prenatal care than similar patients enrolled in commercial plans.

DUNDEE, Scotland -- A five-month course of the ACE inhibitor perindopril (Aceon) was equivalent to six months of exercise training for elderly patients with mobility problems, researchers here found.

LEUVEN, Belgium -- Night-time and day-time blood pressure predicts different cardiovascular endpoints, according to a large multinational study.

MELBOURNE, Australia -- An angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor reduced aortic stiffness and dilation in Marfan's patients taking standard beta-blockers, according to a preliminary study.