A 12-year-old boy presented with a 6-month history of a papule on the corona of the glans penis. The lesion was asymptomatic.

A 12-year-old boy presented with a 6-month history of a papule on the corona of the glans penis. The lesion was asymptomatic.
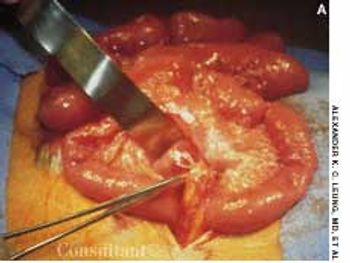
Adhesions can form within the peritoneal cavity after abdominal surgery, especially if there is an underlying inflammatory condition such as appendicitis or inflammatory bowel disease. The incidence of adhesive intestinal obstruction following a laparotomy is approximately 2%. Most adhesive obstructions occur within 3 months of the laparotomy, and 80% occur within 2 years. Adhesive obstructions tend to be more common in children than in adults.

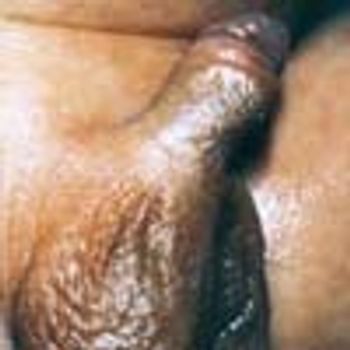
The mother of a 6-year-old boy was concerned because there was a whitish mass between the glans and foreskin of her son's penis. She thought that this might be an accumulation of “pus.”

During the last few weeks of gestationor shortly after birth, the layersof the processus vaginalis normallyfuse together and obliterate the entranceto the inguinal canal in thevicinity of the internal inguinal ring.An indirect hernia results from a failureof fusion of the processus vaginalis;the bowel subsequently descendsthrough the inguinal canal.

Affected infants present shortly afterbirth with a large bowel obstructionsecondary to transient dysmotility inthe descending colon. Although thecause is unknown, immaturity of thecolonic myenteric plexuses has beendemonstrated in some cases. Morethan 50% of affected infants are bornto mothers with diabetes. Other predisposingfactors include hypoglycemiaand sepsis.

The extent of mucosal or transmural intestinal necrosis varies. Pneumatosis progresses from the submucosa through the muscular layer to the subserosa. The distal ileum and proximal colon are most frequently involved.

This condition, which accounts forabout 30% of cases of intestinal obstructionamong neonates, is characterizedby the inspissation of thick,tenacious meconium in the bowel.The most common cause is cystic fibrosis;approximately 6% to 20% of infantswith cystic fibrosis have meconiumileus. Hyperviscous mucus secretedby abnormal intestinal glands,an abnormal concentrating processin the proximal small intestine, and adeficiency of pancreatic enzymeshave been implicated in the pathogenesis.The histologic hallmark is distention of the gobletcells in the intestinal mucosa.

Inspissated, sticky, immobile meconiumcauses this transient form of distalcolonic or rectal obstruction in newborns.The incidence has been estimatedat 1 in 500 to 1000 live births.The condition is thought to resultfrom dehydration of the meconium.

This condition is characterized bya localized narrowing of the jejunumwithout a disruption of continuityor defect in the mesentery. At thestenotic site, there is often a short,narrow segment with a minute lumenwhere the muscularis is irregularand the submucosa is thickened.The resultant intestinal obstructionis incomplete.

This condition involves the invagination of a proximalsegment of bowel (the intussusceptum) into a more distalsegment (the intussuscipiens) (A). It occurs mostfrequently in infants between the ages of 5 and 12months and is a leading cause of intestinal obstructionin children aged 2 months to 5 years. Intrauterine intussusceptionis associated with the development of intestinalatresia. The male to female ratio is approximately3:2. Intussusception is slightly more common in whitethan in black children and is often seen in childrenwith cystic fibrosis.

This obstruction is caused by a failure of intestinal peristalsis;there is no evidence of mechanical obstruction.Paralytic ileus is common after abdominal surgery, especiallyif anticholinergic drugs are given preoperativelyand/or narcotics are used postoperatively. It usually lasts2 to 3 days. Paralytic ileus may also be caused by peritonitis;ischemia or surgical manipulation of the bowel; retroperitonealhemorrhage; spinal fracture; systemic sepsis;shock; hypokalemia; uremia; pharmacologic agents (eg,vincristine, loperamide, and calcium channel blockers);diabetic ketoacidosis; and myxedema.

This obstruction results from hypertrophyof the circular and longitudinalmuscularis of the pylorus and the distalantrum of the stomach. It occursin approximately 3 of every 1000 livebirths and is 4 times more commonin boys. Pyloric stenosis (PS) is relativelyuncommon in African Americanand Asian infants. The observationthat it occurs primarily in first-borninfants has been disputed.

Adhesions (A) can form within theperitoneal cavity after abdominalsurgery, especially if there is an underlyinginflammatory condition suchas appendicitis (B) or inflammatorybowel disease. The incidence of adhesiveintestinal obstruction following alaparotomy is approximately 2%. Mostadhesive obstructions occur within 3months of the laparotomy, and 80%occur within 2 years. Adhesive obstructionstend to be more commonin children than in adults.