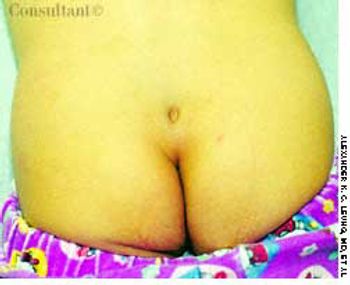
The parents of an 18-month-old girl were curious about a depressed area on their daughter's lower back, which had been present at birth. The child was otherwise healthy.

The parents of an 18-month-old girl were curious about a depressed area on their daughter's lower back, which had been present at birth. The child was otherwise healthy.
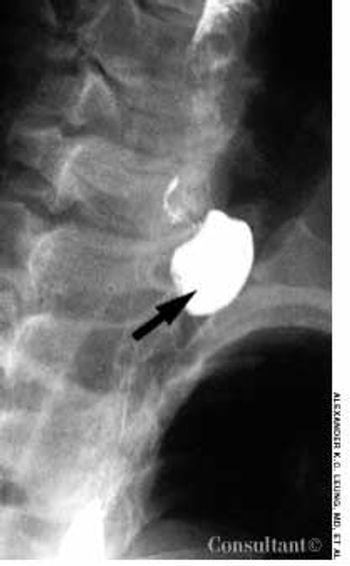
For 8 months, a 69-year-old man had dysphagia, throat irritation, and a recurrent cough. He also complained of a bulge on the left side of the neck that decreased in size when pressed.
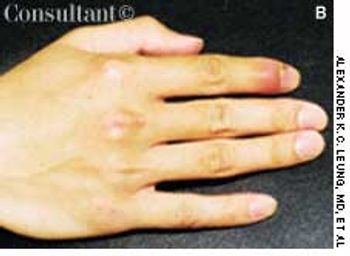
Exquisite pain of 3-days' duration in his right index finger sent a 19-year-old man for medical consultation. He recalled that a thorn had become embedded in the finger while gardening 1 week earlier.
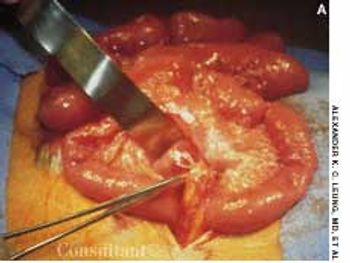
Adhesions can form within the peritoneal cavity after abdominal surgery, especially if there is an underlying inflammatory condition such as appendicitis or inflammatory bowel disease. The incidence of adhesive intestinal obstruction following a laparotomy is approximately 2%. Most adhesive obstructions occur within 3 months of the laparotomy, and 80% occur within 2 years. Adhesive obstructions tend to be more common in children than in adults.

The mother of a 6-year-old boy was concerned because there was a whitish mass between the glans and foreskin of her son's penis. She thought that this might be an accumulation of “pus.”
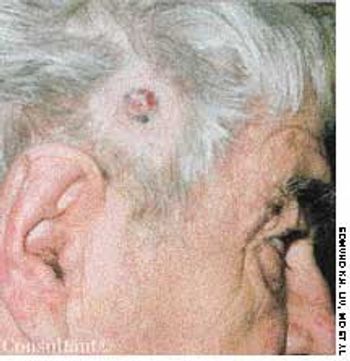
A 67-year-old man had been aware of a painless, firm, red nodule that had been growing slowly on the right temporal area for 1 year. The lesion occasionally bled.
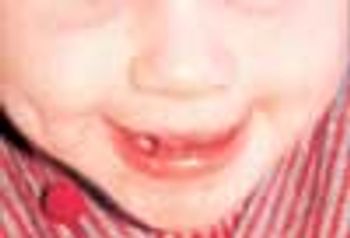
This 20-month-old girl was born to a 28-year-old mother at 38 weeks' gestation. The pregnancy was uncomplicated, and vaginal delivery was normal. The infant sat with support at 10 months of age, sat without support at 12 months, crawled at 13 months, and walked at 18 months. She had not yet begun to talk at 20 months. The child was noted to have frequent laughing episodes and often made flapping movements with her hands.
A 1-year-old girl was noted to have abrasions on the left cheek when she was picked up by her mother from a day-care center. The day-care provider reported that the girl had been bitten on the cheek by a 3-year-old boy during rough play. Her immunization status for tetanus was up-to-date.

A 69-year-old man seen because of a pruritic pretibial rash of 3 months' duration. Started as reddish brown papules that slowly enlarged and changed.

A 3-year-old girl discovered lesions on her instep and great toe, where there was significant pressure from the old rubber sandals that she had been wearing.

During the last few weeks of gestationor shortly after birth, the layersof the processus vaginalis normallyfuse together and obliterate the entranceto the inguinal canal in thevicinity of the internal inguinal ring.An indirect hernia results from a failureof fusion of the processus vaginalis;the bowel subsequently descendsthrough the inguinal canal.

An 18-year-old man presented with a 3-day history of fever, sore throat, and neck swelling. He had previously been healthy, and his immunizations were up-to-date. There was no history of travel outside the country or of an animal bite or scratch.

A 14-year-old boy presented with a 3-day history ofrunny nose, cough, and fever. His temperature was37.7°C (100ºF); heart rate, 78 beats per minute; and respirationrate, 26 breaths per minute. Several symmetric,circular ecchymotic lesions that measured 4 cm in diameterwere noted on the upper chest. There was no evidenceof external injury to other parts of the body. Thechild reported that the bruises resulted from cupping,performed by a Chinese practitioner in an attempt torelieve the fever.

A 7-year-old Chinese boy presented with fever, cough,and sore throat of 2 days’ duration. His temperature was38.3°C (101°F); heart rate, 85 beats per minute; andrespiration rate, 26 breaths per minute. The throat waserythematous but without any exudate. There weresmall cervical lymph nodes bilaterally. The chest wasclear.

This 9-year-old girl had a slightlypruritic perioral rash for 6 months.The skin around her mouth wasred, scaly, thickened, and hyperpigmented.She also had eczematouslesions in the antecubital andpopliteal fossae.

For 2 years, a 66-year-old woman had a winglike structure on the nasal sideof her right eye. She had normal vision. A diagnosis of pterygium was made.
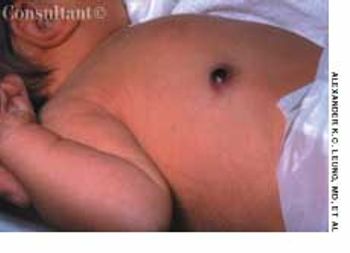
A male infant was born to a 29-year-old woman (gravida 3, para 2), following an uncomplicated pregnancy and normal vaginal delivery. At birth, a brownish 1-cm nodule was noted on the right side of the upper abdomen. The infant was otherwise healthy.

A symptomatic brown macules developed on the face of a 32-year-old woman 1 year ago. She had been taking oral contraceptives for the past 5 years. Her medical history was unremarkable, and the results of a physical examination were normal.

This 17-year-old presented with a 1-month history of weight loss, increased appetite, mild insomnia, hand tremor, palpitations, sweating, heat intolerance, and quick loss of temper. The number of daily bowel movements had increased from 1 to 2. There was no family history of thyroid disorders.

A 17-year-old adolescent experienced an episode of generalized paralysis ofacute onset after physical exertion and consumption of a high-carbohydratemeal. Despite a good appetite, the patient had lost between 2 and 3 lb duringthe past month. He complained of heat intolerance and palpitations and reportedlosing his temper easily.
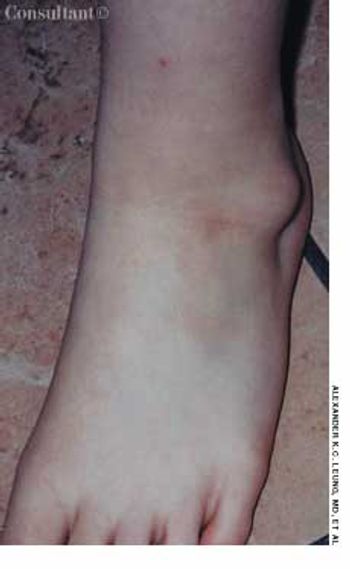
7-year-old boy presented with an asymptomatic cystic lesion on the lateral aspect of the left ankle of 4 months’ duration. There was no history of trauma. The mass fluctuated in size; it was smaller when the child was recumbent and larger when the child was upright.

Affected infants present shortly afterbirth with a large bowel obstructionsecondary to transient dysmotility inthe descending colon. Although thecause is unknown, immaturity of thecolonic myenteric plexuses has beendemonstrated in some cases. Morethan 50% of affected infants are bornto mothers with diabetes. Other predisposingfactors include hypoglycemiaand sepsis.

The extent of mucosal or transmural intestinal necrosis varies. Pneumatosis progresses from the submucosa through the muscular layer to the subserosa. The distal ileum and proximal colon are most frequently involved.

This condition, which accounts forabout 30% of cases of intestinal obstructionamong neonates, is characterizedby the inspissation of thick,tenacious meconium in the bowel.The most common cause is cystic fibrosis;approximately 6% to 20% of infantswith cystic fibrosis have meconiumileus. Hyperviscous mucus secretedby abnormal intestinal glands,an abnormal concentrating processin the proximal small intestine, and adeficiency of pancreatic enzymeshave been implicated in the pathogenesis.The histologic hallmark is distention of the gobletcells in the intestinal mucosa.

Inspissated, sticky, immobile meconiumcauses this transient form of distalcolonic or rectal obstruction in newborns.The incidence has been estimatedat 1 in 500 to 1000 live births.The condition is thought to resultfrom dehydration of the meconium.
A boy was born to a gravida 2, para 1, 26-year-old woman at 37 weeks’ gestation. The pregnancy had been complicated by gestational diabetes. The infant was delivered vaginally; Apgar scores were 6 at 1 minute and 9 at 5 minutes.

This condition is characterized bya localized narrowing of the jejunumwithout a disruption of continuityor defect in the mesentery. At thestenotic site, there is often a short,narrow segment with a minute lumenwhere the muscularis is irregularand the submucosa is thickened.The resultant intestinal obstructionis incomplete.

This condition involves the invagination of a proximalsegment of bowel (the intussusceptum) into a more distalsegment (the intussuscipiens) (A). It occurs mostfrequently in infants between the ages of 5 and 12months and is a leading cause of intestinal obstructionin children aged 2 months to 5 years. Intrauterine intussusceptionis associated with the development of intestinalatresia. The male to female ratio is approximately3:2. Intussusception is slightly more common in whitethan in black children and is often seen in childrenwith cystic fibrosis.

This obstruction is caused by a failure of intestinal peristalsis;there is no evidence of mechanical obstruction.Paralytic ileus is common after abdominal surgery, especiallyif anticholinergic drugs are given preoperativelyand/or narcotics are used postoperatively. It usually lasts2 to 3 days. Paralytic ileus may also be caused by peritonitis;ischemia or surgical manipulation of the bowel; retroperitonealhemorrhage; spinal fracture; systemic sepsis;shock; hypokalemia; uremia; pharmacologic agents (eg,vincristine, loperamide, and calcium channel blockers);diabetic ketoacidosis; and myxedema.

This obstruction results from hypertrophyof the circular and longitudinalmuscularis of the pylorus and the distalantrum of the stomach. It occursin approximately 3 of every 1000 livebirths and is 4 times more commonin boys. Pyloric stenosis (PS) is relativelyuncommon in African Americanand Asian infants. The observationthat it occurs primarily in first-borninfants has been disputed.