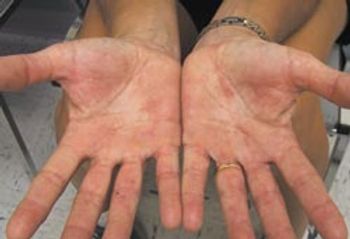
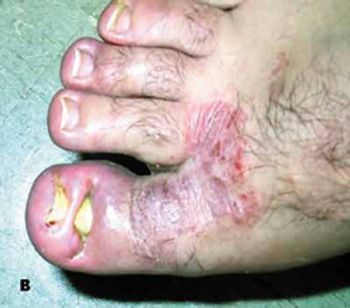
A 79-year-old woman with a 37-year history of type 2 diabetes mellitus complains of head pain that began more thana month ago and is localized to the left frontotemporal region. She characterizes the pain as constant and burning, with minimalfluctuations in intensity. The pain does not increase with any particular activity but is quite disabling; it has causedemotional lability and insomnia. She denies nausea, visual disturbances, weakness of the extremities, dizziness, or tinnitus.Her appetite is depressed; she has experienced some weight loss.