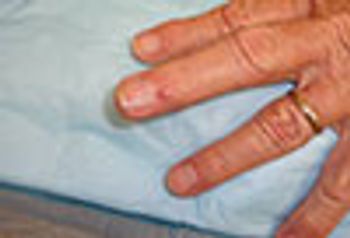
This translucent dark pink nodule located just behind the nail is the classic presentation of a digital myxoid cyst.

This translucent dark pink nodule located just behind the nail is the classic presentation of a digital myxoid cyst.
A rapidly developing lesion . . . flashing lights . . . blue sclera: can you answer this week’s 5 quiz questions?
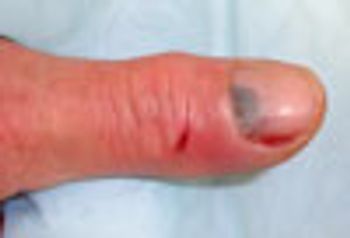
After a dog bite, trauma in the form of a subungual hematoma and shallow lacerations prompted a 10-day course of amoxicillin-clavulanate. This antibiotic is also useful for cat and human bites that appear to be at high risk of becoming infected.
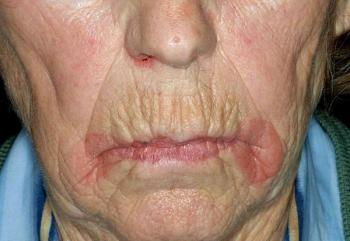
Read carefully this week: you'll find helpful clues in at least 3 of the descriptions . . .
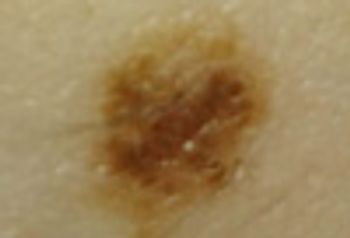
Here: short cases with photos that show melanoma, and pigmented lesions that mimic melanoma.
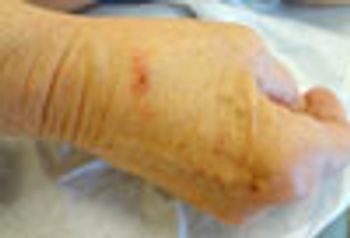
A biopsy revealed non-caseating granulomata, and culture revealed Mycobacterium marinum. This patient had a fish tank at home, and used his right hand to perform maintenance.
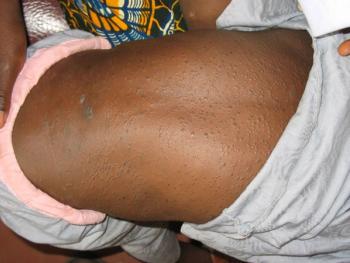
Go for the Glory Quiz - Does this rash suggest something more than skin deep? Diabetes and CKD? Scrotal lesions? See if you can answer all 5 quiz questions.
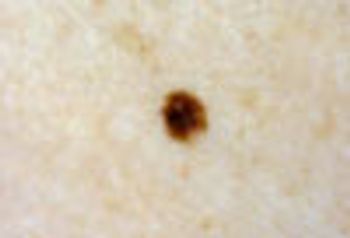
This pigmented macule clearly stands out against a bland background of fair-complected skin. This is known as the “ugly duckling” sign. Such lesions should always be viewed with suspicion and a biopsy is generally indicated.
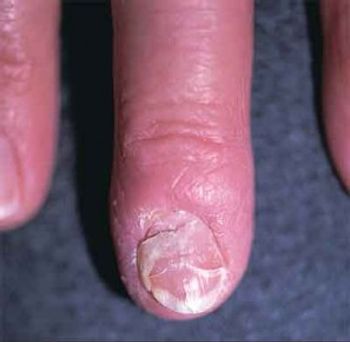
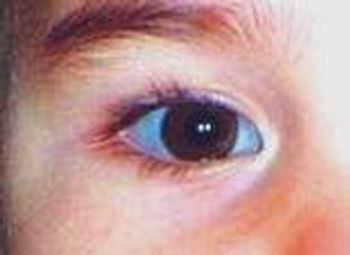
Is thyroid hormone medication associated with nail plate deformity, or is something else going on?
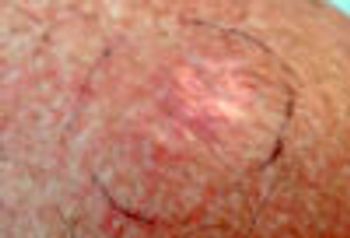
This tumor is a low-grade soft tissue sarcoma. Metastases are uncommon, but local recurrence is very frequent. Mohs surgery is the optimal treatment modality.
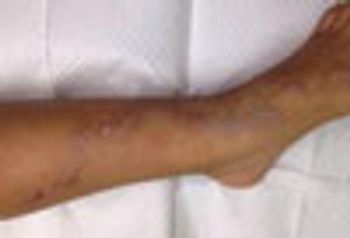
Cutaneous larva migrans (CLM), also known as “creeping eruption,” is the most commonly acquired tropical dermatosis
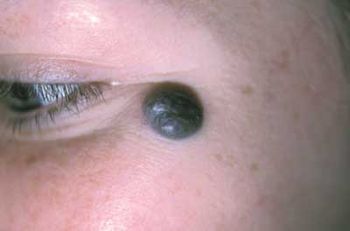
Recent trauma caused this lesion, which had been present since the patient’s birth, to enlarge. What is it?
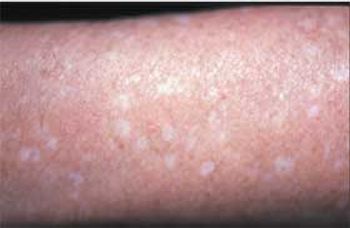
Images of guttate hypomelanosis, jellyfish sting, basal cell carcinoma, cercarial dermatitis (swimmer’s itch), epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor photosensitivity (sunburn), seabather’s eruption, and squamous cell carcinoma.
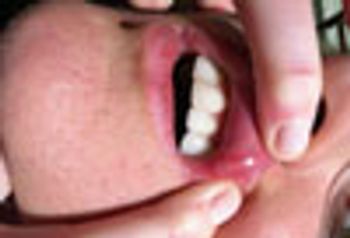
The shallow ulceration surrounded by a ring of erythema is characteristic for aphthous ulcers (canker sores). This patient’s otherwise negative history rules out Behcet’s disease.
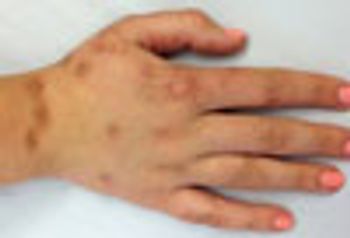
The persistent pigmentation on this woman’s hands corresponds to areas of intralesional injections of bleomycin for recalcitrant warts.
This week’s questions challenge your dermatologic and radiologic skills, and then some. See how you fare…

The diagnosis of juvenile dermatomyositis can be challenging when proximal muscle weakness develops without characteristic skin manifestations. In this patient, rash appeared 2 months after the onset of muscle weakness. As a result, the initial diagnosis was viral myositis, which led to delayed therapy.
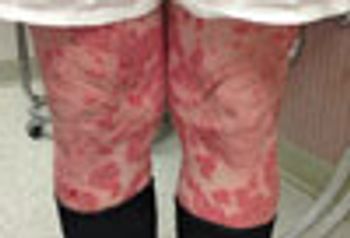
Adult-onset psoriasis is uncommon without a precipitating factor. In this patient’s case, an oral beta-blocker precipitated the psoriasis.
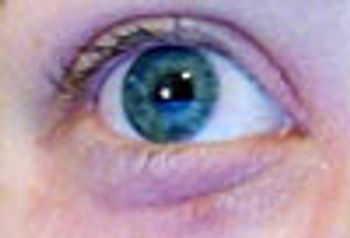
Contact dermatitis to paste-on fingernail decorations developed when the patient held her lower eyelid down with her index finger to insert her contact lenses.
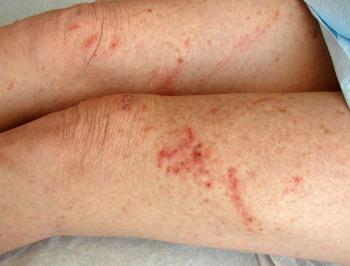
Images of acute allergic contact dermatitis, Lyme disease, southern tick–associated rash illness, tick-borne babesiosis, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and brown recluse spider bites.

There are 3.5 million cases of skin cancer each year, which is more than new cases of breast, prostate, lung, and colon cancers combined.

Melanoma in pre-adolescent children is extremely rare, but not totally unknown. Because this lesion had recently become larger and darker, the lesion was excised; histology confirmed a benign nevus.
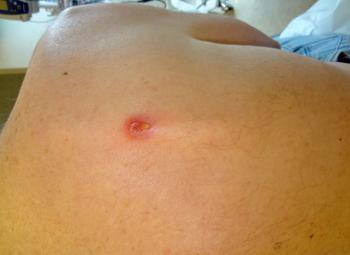
Which organism is the likely cause of this lesion? Can you pick up dx clues in this sonogram? Test your clinical skills here with this week’s 5-question quiz...

Is this lesion the result of an injury, as the boy’s mother suspected, or something else?
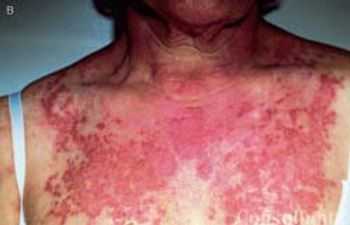
Images of guttate, small-plaque, and chronic plaque psoriasis; systemic lupus erythematosus; pityriasis rubra pilaris; and secondary syphilis.